Spontaneously arising red cells with a McLeod-like phenotype in normal donors
- PMID: 19909712
- PMCID: PMC2794671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.03.009
Spontaneously arising red cells with a McLeod-like phenotype in normal donors
Abstract
Very few human genes can be used to identify spontaneous inactivating somatic mutations. We hypothesized that because the XK gene is X-linked, it would be easy to identify spontaneously arising red cells with a phenotype resembling the McLeod syndrome, which results from inherited XK mutations. Here, by flow cytometry, we detect such phenotypic variants at a median frequency of 9 x 10(-6) in neonatal cord blood samples and 39 x 10(-6) in healthy adults (p=0.004). It may be possible to further investigate the relationship between aging, mutations, and cancer using this approach.
Figures
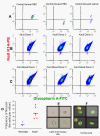
References
-
- Morley A, Trainor K, Seshadri R, Ryall R. Measurement of in vivo mutations in human lymphocytes. Nature. 1983;302:155–156. - PubMed
-
- Albertini R, Nicklas J, O’Neill J, Robison S. In vivo somatic mutations in humans: measurement and analysis. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:305–326. - PubMed
-
- Grist S, McCarron M, Kutlaca A, Turner D, Morley A. In vivo human somatic mutation: frequency and spectrum with age. Mutation Research. 1992;266:189–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

