Antimetastatic role of Smad4 signaling in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 19909744
- PMCID: PMC2831103
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.11.004
Antimetastatic role of Smad4 signaling in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background & aims: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling occurs through Smads 2/3/4, which translocate to the nucleus to regulate transcription; TGF-beta has tumor-suppressive effects in some tumor models and pro-metastatic effects in others. In patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), mutations or reduced levels of Smad4 have been correlated with reduced survival. However, the function of Smad signaling and the effects of TGF-beta-receptor kinase inhibitors have not been analyzed during CRC metastasis. We investigated the role of TGF-beta/Smad signaling in CRC progression.
Methods: We evaluated the role of TGF-beta/Smad signaling on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, tumorigenicity, and metastasis in Smad4-null colon carcinoma cell lines (MC38 and SW620) and in those that transgenically express Smad4. We also determined the effects of a TGF-beta-receptor kinase inhibitor (LY2109761) in CRC tumor progression and metastasis in mice.
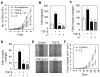
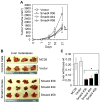
Results: TGF-beta induced migration/invasion, tumorigenicity, and metastasis of Smad4-null MC38 and SW620 cells; incubation with LY2109761 reversed these effects. In mice, LY2109761 blocked metastasis of CRC cells to liver, inducing cancer cell expression of E-cadherin and reducing the expression of the tumorigenic proteins matrix metalloproteinase-9, nm23, urokinase plasminogen activator, and cyclooxygenase-2. Transgenic expression of Smad4 significantly reduced the oncogenic potential of MC38 and SW620 cells; in these transgenic cells, TGF-beta had tumor suppressor, rather than tumorigenic, effects.
Conclusions: TGF-beta/Smad signaling suppresses progression and metastasis of CRC cells and tumors in mice. Loss of Smad4 might underlie the functional shift of TGF-beta from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter; inhibitors of TGF-beta signaling might be developed as CRC therapeutics.
Copyright 2009 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Derynck R, Zhang YE. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature. 2003;425:577–584. - PubMed
-
- Datta PK, Mann JR. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF- β) signling inhibitrs in cancer therapy. In: Jakowlew SB, editor. Transforming Growth Factor-β in Cancer Therapy. 1. Vol. 2. Totowa: Humana Press; 2007. pp. 573–588.
-
- Bandyopadhyay A, Agyin JK, Wang L, et al. Inhibition of pulmonary and skeletal metastasis by a transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6714–6721. - PubMed
-
- Ge R, Rajeev V, Ray P, et al. Inhibition of growth and metastasis of mouse mammary carcinoma by selective inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4315–4330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

