Epigenetic regulation of caspase-3 gene expression in rat brain development
- PMID: 19909801
- PMCID: PMC2795079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.10.008
Epigenetic regulation of caspase-3 gene expression in rat brain development
Abstract
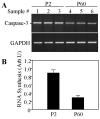
The expression levels of caspase-3, a major contributor to the execution of neuronal apoptosis, markedly decrease in the process of brain maturation. We have previously cloned the rat caspase-3 gene promoter and identified its essential regulatory elements. In the present study, we extended previous findings by examining transcriptional regulation of caspase-3 expression in the rat brain of two different ages, corresponding to the immature and mature brain. In particular, we determined that the rate of transcription initiation substantially declines during brain maturation. Furthermore, we established that mRNA levels of Ets1, Ets2, and Sp1 do not change in the brain with maturation, suggesting that these transcription factors do not contribute to age-dependent caspase-3 down-regulation. Hence, we examined a role of DNA methylation and histone modification in this process. Utilizing bisulfite DNA sequencing, we determined the presence of age-dependent differentially methylated fragments within the caspase-3 promoter region. Strikingly, differentially methylated CpG sites correspond to the predicted binding sites for a number of transcription factors that have been previously shown to be involved in neuronal development and differentiation. Moreover, using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we found that mature brains displayed significantly lower levels of histone 3 acetylated Lys14 and histone 4 acetylated Lys5, 8, 12, and 16. This observation is consistent with the decreased level of expression of caspase-3 in the mature brain. Together with our observation that histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin A, increased the level of caspase-3 mRNA in cortical neurons in vitro, these results further indicate an important role of epigenetic factors in the regulation of caspase-3 gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulation of thy-1 by histone deacetylase inhibitor in rat lung fibroblasts.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Jul;45(1):16-23. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0154OC. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20724553 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated changes in DNA methylation and histone modifications regulate silencing/derepression of luteinizing hormone receptor gene transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(18):7929-39. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.7929-7939.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16135786 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate the transcriptional regulation of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-a gene: interactive roles of modified histones, histone acetyltransferase, p300, AND Sp1.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6991-7002. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511444. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24451378 Free PMC article.
-
MDR1 promoter hypermethylation in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: changes in chromatin structure induced by treatment with 5-Aza-cytidine.Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Jun;3(6):540-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.3.6.845. Epub 2004 Jun 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15034303
-
Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A on epigenetic changes and transcriptional activation of Bdnf promoter 1 by rat hippocampal neurons.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jun;1199:186-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05175.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20633124
Cited by
-
Chromatin modifying agents in the in vitro production of bovine embryos.Vet Med Int. 2010 Sep 29;2011:694817. doi: 10.4061/2011/694817. Vet Med Int. 2010. PMID: 20936105 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-138-5p Upregulation during Neuronal Maturation Parallels with an Increase in Neuronal Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 20;24(22):16509. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216509. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003699 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of neonatal brain injury.Neurol Res Int. 2012;2012:506320. doi: 10.1155/2012/506320. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Neurol Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22363841 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetylation and its role in embryonic stem cell differentiation.World J Stem Cells. 2010 Dec 26;2(6):121-6. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v2.i6.121. World J Stem Cells. 2010. PMID: 21607129 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death atlas of the postnatal mouse ventral forebrain and hypothalamus: effects of age and sex.J Comp Neurol. 2013 Aug 1;521(11):2551-69. doi: 10.1002/cne.23298. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23296992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alnemri ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW, Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW, Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell. 1996;87:171. - PubMed
-
- Baylin SB, Esteller M, Rountree MR, Bachman KE, Schuebel K, Herman JG. Aberrant patterns of DNA methylation, chromatin formation and gene expression in cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:687–692. - PubMed
-
- Boutillier AL, Trinh E, Loeffler JP. Constitutive repression of E2F1 transcriptional activity through HDAC proteins is essential for neuronal survival. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;973:438–442. - PubMed
-
- Bruggemeier U, Kalff M, Franke S, Scheidereit C, Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991;64:565–572. - PubMed
-
- Callaerts P, Halder G, Gehring WJ. PAX-6 in development and evolution. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:483–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

