When children with Kawasaki disease grow up: Myocardial and vascular complications in adulthood
- PMID: 19909870
- PMCID: PMC2870533
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.102
When children with Kawasaki disease grow up: Myocardial and vascular complications in adulthood
Abstract
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute, self-limited vasculitis that typically occurs in young children and was first described by Japanese pediatrician Tomisaku Kawasaki in 1967. Although originally thought to be a rare condition, KD has become the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the pediatric age group in developed countries. The majority of patients with KD appear to have a benign prognosis, but a subset of patients with coronary artery aneurysms are at risk for ischemic events and require lifelong treatment. In the 4 decades that have passed since the initial recognition of KD, the number of patients reaching adulthood has continued to grow. Adult cardiologists will be increasingly involved in the management of these patients. Currently, there are no established guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of adult patients who have had KD. We review here the current literature that may be helpful to clinicians who care for adults who experienced KD in childhood.
Figures
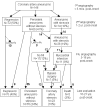

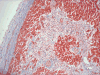
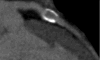
Comment in
-
Not just coronary arteritis, Kawasaki disease is a myocarditis, too.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010 Apr 6;55(14):1507; author reply 1507-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.11.067. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20359606 No abstract available.
References
-
- Taubert KA, Rowley AH, Shulman ST. Nationwide survey of Kawasaki disease and acute rheumatic fever. J Pediatr. 1991;119:279–82. - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki T, Kosaki F, Okawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa H. A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics. 1974;54:271–6. - PubMed
-
- Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, et al. Long-term consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10- to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation. 1996;94:1379–85. - PubMed
-
- Burns JC, Glode MP. Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet. 2004;364:533–44. - PubMed
-
- Senzaki H. Long-term outcome of Kawasaki disease. Circulation. 2008;118:2763–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

