Hypereosinophilic syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy
- PMID: 19910029
- PMCID: PMC2829669
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.022
Hypereosinophilic syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy
Abstract
Background: Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a heterogeneous group of rare disorders defined by persistent blood eosinophilia > or =1.5 x 10(9)/L, absence of a secondary cause, and evidence of eosinophil-associated pathology. With the exception of a recent multicenter trial of mepolizumab (anti-IL-5 mAb), published therapeutic experience has been restricted to case reports and small case series.
Objective: The purpose of the study was to collect and summarize baseline demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics in a large, diverse cohort of patients with HES and to review responses to treatment with conventional and novel therapies.
Methods: Clinical and laboratory data from 188 patients with HES, seen between January 2001 and December 2006 at 11 institutions in the United States and Europe, were collected retrospectively by chart review.
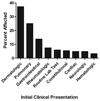
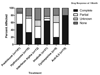
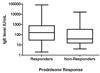
Results: Eighteen of 161 patients (11%) tested were Fip1-like 1-platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (FIP1L1-PDGFRA) mutation-positive, and 29 of 168 patients tested (17%) had a demonstrable aberrant or clonal T-cell population. Corticosteroid monotherapy induced complete or partial responses at 1 month in 85% (120/141) of patients with most remaining on maintenance doses (median, 10 mg prednisone equivalent daily for 2 months to 20 years). Hydroxyurea and IFN-alpha (used in 64 and 46 patients, respectively) were also effective, but their use was limited by toxicity. Imatinib (used in 68 patients) was more effective in patients with the FIP1L1-PDGFRA mutation (88%) than in those without (23%; P < .001).
Conclusion: This study, the largest clinical analysis of patients with HES to date, not only provides useful information for clinicians but also should stimulate prospective trials to optimize treatment of HES.
Figures



Comment in
-
Heterogeneity among characteristics of hypereosinophilic syndromes.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Jun;125(6):1399-1401.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.02.024. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20392489 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975;54:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Weller PF, Bubley GJ. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 1994;83:2759–2779. - PubMed
-
- Simon HU, Plotz SG, Dummer R, Blaser K. Abnormal clones of T cells producing interleukin-5 in idiopathic eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1112–1120. - PubMed
-
- Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Stover EH, Legare RD, Cortes J, et al. A novel tyrosine kinase created by the fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes is a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1201–1214. - PubMed
-
- Klion AD, Noel P, Akin C, Law MA, Gilliland DG, Cools J, et al. Elevated serum tryptase levels identify a subset of patients with a myeloproliferative variant of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome associated with tissue fibrosis, poor prognosis and imatinib-responsiveness. Blood. 2003;101:4660–4666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

