Elevations in ostensibly anabolic hormones with resistance exercise enhance neither training-induced muscle hypertrophy nor strength of the elbow flexors
- PMID: 19910330
- PMCID: PMC2885075
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01147.2009
Elevations in ostensibly anabolic hormones with resistance exercise enhance neither training-induced muscle hypertrophy nor strength of the elbow flexors
Abstract
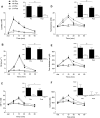
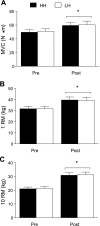
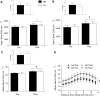
The aim of our study was to determine whether resistance exercise-induced elevations in endogenous hormones enhance muscle strength and hypertrophy with training. Twelve healthy young men (21.8 +/- 1.2 yr, body mass index = 23.1 +/- 0.6 kg/m(2)) trained their elbow flexors independently for 15 wk on separate days and under different hormonal milieu. In one training condition, participants performed isolated arm curl exercise designed to maintain basal hormone concentrations (low hormone, LH); in the other training condition, participants performed identical arm exercise to the LH condition followed immediately by a high volume of leg resistance exercise to elicit a large increase in endogenous hormones (high hormone, HH). There was no elevation in serum growth hormone (GH), insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), or testosterone after the LH protocol but significant (P < 0.001) elevations in these hormones immediately and 15 and 30 min after the HH protocol. The hormone responses elicited by each respective exercise protocol late in the training period were similar to the response elicited early in the training period, indicating that a divergent postexercise hormone response was maintained over the training period. Muscle cross-sectional area (CSA) increased by 12% in LH and 10% in HH (P < 0.001) with no difference between conditions (condition x training interaction, P = 0.25). Similarly, type I (P < 0.01) and type II (P < 0.001) muscle fiber CSA increased with training with no effect of hormone elevation in the HH condition. Strength increased in both arms, but the increase was not different between the LH and HH conditions. We conclude that exposure of loaded muscle to acute exercise-induced elevations in endogenous anabolic hormones enhances neither muscle hypertrophy nor strength with resistance training in young men.
Figures
References
-
- Adams GR. Autocrine/paracrine IGF-I and skeletal muscle adaptation. J Appl Physiol 93: 1159–1167, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Baar K, Esser K. Phosphorylation of p70(S6k) correlates with increased skeletal muscle mass following resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 276: C120–C127, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Bhasin S, Storer TW, Berman N, Callegari C, Clevenger B, Phillips J, Bunnell TJ, Tricker R, Shirazi A, Casaburi R. The effects of supraphysiologic doses of testosterone on muscle size and strength in normal men. N Engl J Med 335: 1–7, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Buresh R, Berg K, French J. The effect of resistive exercise rest interval on hormonal response, strength, and hypertrophy with training. J Strength Cond Res 23: 62–71, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Carroll TJ, Herbert RD, Munn J, Lee M, Gandevia SC. Contralateral effects of unilateral strength training: evidence and possible mechanisms. J Appl Physiol 101: 1514–1522, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

