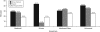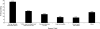Association of race, substance abuse, and health insurance coverage with use of highly active antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected women, 2005
- PMID: 19910347
- PMCID: PMC2901300
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.158949
Association of race, substance abuse, and health insurance coverage with use of highly active antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected women, 2005
Abstract
Objectives: We examined racial/ethnic disparities in highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) use and whether differences are moderated by substance use or insurance status, using data from the Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS).
Methods: Logistic regression examined HAART use in a longitudinal cohort of women for whom HAART was clinically indicated in 2005 (N = 1354).
Results: Approximately 3 of every 10 eligible women reported not taking HAART. African American and Hispanic women were less likely than were White women to use HAART. After we adjusted for potential confounders, the higher likelihood of not using HAART persisted for African American but not for Hispanic women. Uninsured and privately insured women, regardless of race/ethnicity, were less likely than were Medicaid enrollees to use HAART. Although alcohol use was related to HAART nonuse, illicit drug use was not.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that expanding and improving insurance coverage should increase access to antiretroviral therapy across racial/ethnic groups, but it is not likely to eliminate the disparity in use of HAART between African American and White women with HIV/AIDS.
Figures
References
-
- Palella FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med 1998;338(13):853–860 - PubMed
-
- Shapiro MF, Morton SC, McCaffrey D, et al. Variations in the care of HIV-infected adults in the United States. JAMA 1999;281(24):2305–2315 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham WE, Mardson LW, Andersen RM, et al. Prevalence and predictors of highly active antiretroviral therapy use in patients with HIV infection in the United States. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2000;25(2):115–123 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UO1-HD-32632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA022971/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-42590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-31834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States