Histone variant H2A.Z regulates centromere silencing and chromosome segregation in fission yeast
- PMID: 19910462
- PMCID: PMC2804349
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.058487
Histone variant H2A.Z regulates centromere silencing and chromosome segregation in fission yeast
Abstract
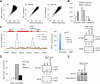
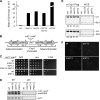
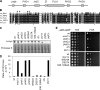
The incorporation of histone variant H2A.Z into nucleosomes plays essential roles in regulating chromatin structure and gene expression. A multisubunit complex containing chromatin remodeling protein Swr1 is responsible for the deposition of H2A.Z in budding yeast and mammals. Here, we show that the JmjC domain protein Msc1 is a novel component of the fission yeast Swr1 complex and is required for Swr1-mediated incorporation of H2A.Z into nucleosomes at gene promoters. Loss of Msc1, Swr1, or H2A.Z results in loss of silencing at centromeres and defective chromosome segregation, although centromeric levels of CENP-A, a centromere-specific histone H3 variant that is required for setting up the chromatin structure at centromeres, remain unchanged. Intriguingly, H2A.Z is required for the expression of another centromere protein, CENP-C, and overexpression of CENP-C rescues centromere silencing defects associated with H2A.Z loss. These results demonstrate the importance of H2A.Z and CENP-C in maintaining a silenced chromatin state at centromeres.
Figures



References
-
- Cleveland D. W., Mao Y., Sullivan K. F. (2003) Cell 112, 407–421 - PubMed
-
- Malik H. S., Henikoff S. (2009) Cell 138, 1067–1082 - PubMed
-
- Allis C., Jenuwein T., Reinberg D. (2006) Epigenetics, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
-
- Black B. E., Foltz D. R., Chakravarthy S., Luger K., Woods V. L., Jr., Cleveland D. W. (2004) Nature 430, 578–582 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

