Metabolism of very-low-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein containing apolipoprotein C-III and not other small apolipoproteins
- PMID: 19910636
- PMCID: PMC2818784
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.197830
Metabolism of very-low-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein containing apolipoprotein C-III and not other small apolipoproteins
Erratum in
- Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2010 Sep;30(9):e171
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to clarify the influence of apolipoprotein C-III (apoCIII) on human apolipoprotein B metabolism.
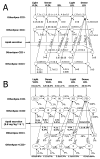
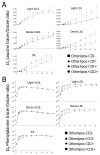
Methods and results: We studied the kinetics of 4 very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) types containing: (1) otherApos-CIII-: none of apoCIII, apoAII, apoCI, apoCII, or apoE; (2) otherApos+CIII-: no apoCIII but at least one of the others; (3) otherApos-CIII+: apoCIII, but not any others; and (4) otherApos+CIII+: apoCIII and at least one other. VLDL and IDL otherApos-CIII+ and otherApos-CIII- had similar rates of lipolytic conversion to smaller particles. However, light LDL otherApos-CIII+ compared with otherApos-CIII- had much faster conversion to dense LDL as did light LDL otherApos+CIII+ compared with otherApos+CIII-. VLDL and IDL otherApos-CIII+ had minimal direct removal from circulation, whereas VLDL and IDL otherApos+CIII-, rich in apoE, showed fast clearance. Lipoproteins in fraction otherApos+CIII+ also rich in apoE had very low clearance.
Conclusions: The results suggest that apoCIII strongly inhibits hepatic uptake of VLDL and IDL overriding the opposite influence of apoE when both are present. The presence of apoCIII on dense VLDL is not associated with slow conversion to IDL, a lipoprotein lipase-dependent process; but when on light LDL, apoCIII is associated with enhanced conversion to dense LDL, a process involving hepatic lipase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
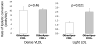

References
-
- Ooi EM, Barrett PH, Chan DC, Watts GF. Apolipoprotein C-III: understanding an emerging cardiovascular risk factor. Clin Science. 2008;114:611–624. - PubMed
-
- Pollin TI, Damcott CM, Shen H, Ott SH, Shelton J, Horenstein RB, Post W, McLenithan JC, Bielak LF, Peyser PA, Mitchell BD, Miller M, O’Connell JR, Shuldiner AR. A null mutation in human APOC3 confers a favorable plasma lipid profile and apparent cardioprotection. Science. 2008;322:1702–1705. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown WV, Baginsky ML. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972;46:375–382. - PubMed
-
- Havel RJ, Fielding CJ, Olivecrona T, Shore VG, Fielding PE, Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973;12:1828–1833. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg HN, Le NA, Goldberg IJ, Gibson JC, Rubinstein A, Wang-Iverson P, Norum R, Brown WV. Apolipoprotein B metabolism in subjects with deficiency of apolipoproteins CIII and AI. Evidence that apolipoprotein CIII inhibits catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1986;78:1287–1295. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

