Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 closes the CFTR Cl channel, but has no effect on the cystic fibrosis mutant deltaF508-CFTR
- PMID: 19910675
- PMCID: PMC2795324
- DOI: 10.1159/000257427
Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 closes the CFTR Cl channel, but has no effect on the cystic fibrosis mutant deltaF508-CFTR
Abstract
Background: Deletion of phenylalanine-508 (DeltaF508) from the first nucleotide-binding domain (NBD1) in the wild-type cystic fibrosis (CF) transmembrane-conductance regulator (wtCFTR) causes CF. However, the mechanistic relationship between DeltaF508-CFTR and the diversity of CF disease is unexplained. The surface location of F508 on NBD1 creates the potential for protein-protein interactions and nearby, lies a consensus sequence (SYDE) reported to control the pleiotropic protein kinase CK2.
Methods: Electrophysiology, immunofluorescence and biochemistry applied to CFTR-expressing cells, Xenopus oocytes, pancreatic ducts and patient biopsies.
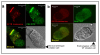
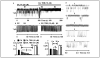
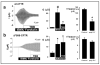
Results: Irrespective of PKA activation, CK2 inhibition (ducts, oocytes, cells) attenuates CFTR-dependent Cl(-) transport, closing wtCFTR in cell-attached membrane patches. CK2 and wtCFTR co-precipitate and CK2 co-localized with wtCFTR (but not DeltaF508-CFTR) in apical membranes of human airway biopsies. Comparing wild-type and DeltaF508CFTR expressing oocytes, only DeltaF508-CFTR Cl(-) currents were insensitive to two CK2 inhibitors. Furthermore, wtCFTR was inhibited by injecting a peptide mimicking the F508 region, whereas the DeltaF508-equivalent peptide had no effect.
Conclusions: CK2 controls wtCFTR, but not DeltaF508-CFTR. Others find that peptides from the F508 region of NBD1 allosterically control CK2, acting through F508. Hence, disruption of CK2-CFTR interaction by DeltaF508-CFTR might disrupt multiple, membrane-associated, CK2-dependent pathways, creating a new molecular disease paradigm for deleted F508 in CFTR.
2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures




References
-
- Kerem B, Rommens JM, Buchanan JA, Markiewicz D, Cox TK, Chakravarti A, Buchwald M, Tsui L-C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989;245:1073–1080. - PubMed
-
- Welsh MJ, Ramsey BW, Accurso F, Cutting GR. Cystic fibrosis. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill Inc.; New York: 2001. pp. 5121–5188.
-
- Sheppard DN, Welsh MJ. Structure and function of the CFTR chloride channel. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:S23–45. - PubMed
-
- Riordan JR. Assembly of functional CFTR chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:701–718. - PubMed
-
- Holland IB, Cole SPC, Kuchler K, Higgins CF. ABC Proteins: From Bacteria to Man. Academic Press; London: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
