Carbon tetrachloride affects inflammation-related biochemical networks in the mouse liver as identified by a customized cDNA microarray system
- PMID: 19911120
- PMCID: PMC2824101
- DOI: 10.1007/s12199-009-0117-6
Carbon tetrachloride affects inflammation-related biochemical networks in the mouse liver as identified by a customized cDNA microarray system
Abstract
Objectives: We have attempted to upgrade and validate an in-house cDNA microarray system developed by our group for the evaluation of chemical toxicity.
Methods: To establish an in-house microarray, we selected genes that play pivotal roles in detoxifying exogenous substances and maintaining homeostasis in the liver. To validate the system, we examined gene expression profiles in mouse liver following treatment with different doses of carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)). The data were also analyzed by pathway analysis tools.
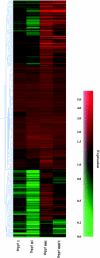
Results: We upgraded our array system by collecting genes that are responsive to xenobiotic receptors, apoptosis-related genes, and stress-responsive genes. The acute toxicity of CCl(4) was confirmed by elevated levels of serum transaminase and histopathological findings. The microarray data showed the CCl(4) treatment induced significant changes in gene expression in the mouse liver, and the ingenuity pathways analysis revealed alterations in gene expression in inflammation-related networks.
Conclusions: We have established a focused microarray system that may be useful for use in toxicogenomics studies. Using this array system, we gained insight into the mechanisms by which CCl(4) exerts its toxic effects. The results of our study also indicate that the combination of focused arrays and bioinformatics tools is helpful in the mechanistic analysis of chemical toxicity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression profile of liver genes in response to hepatotoxicants identified using a SAGE-based customized DNA microarray system.Toxicol Lett. 2008 Feb 28;177(1):20-30. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.12.004. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Toxicol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18243596
-
Transcriptome responses to carbon tetrachloride and pyrene in the kidney and liver of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Aquat Toxicol. 2005 Aug 15;74(1):70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.04.009. Aquat Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15963578
-
Changes in the gene expression associated with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis persist after cessation of dosing in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2004 Jun;79(2):404-10. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh120. Epub 2004 Mar 31. Toxicol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15056808
-
The Liver Protection Effects of Maltol, a Flavoring Agent, on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Apoptosis and Inflammatory Response.Molecules. 2018 Aug 23;23(9):2120. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092120. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30142916 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative studies in toxicogenomics in rodent liver in JEMS·MMS; a useful application of principal component analysis on toxicogenomics.Genes Environ. 2016 Aug 1;38:15. doi: 10.1186/s41021-016-0041-0. eCollection 2016. Genes Environ. 2016. PMID: 27482301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and analysis of differently expressed transcription factors in aristolochic acid nephropathy.Environ Health Prev Med. 2024;29:30. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.23-00245. Environ Health Prev Med. 2024. PMID: 38777778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas RS, Rank DR, Penn SG, Zastrow GM, Hayes KR, Pande K, et al. Identification of toxicologically predictive gene sets using cDNA microarrays. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;60:1189–1194. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
