Role of Epiprofin, a zinc-finger transcription factor, in limb development
- PMID: 19913006
- PMCID: PMC3538143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.11.007
Role of Epiprofin, a zinc-finger transcription factor, in limb development
Abstract
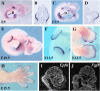
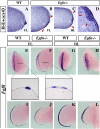
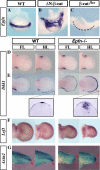
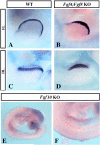
The formation and maintenance of the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is critical for the outgrowth and patterning of the vertebrate limb. In the present work, we have investigated the role of Epiprofin (Epfn/Sp6), a member of the SP/KLF transcription factor family that is expressed in the limb ectoderm and the AER, during limb development. Epfn mutant mice have a defective autopod that shows mesoaxial syndactyly in the forelimb and synostosis (bony fusion) in the hindlimb and partial bidorsal digital tips. Epfn mutants also show a defect in the maturation of the AER that appears flat and broad, with a double ridge phenotype. By genetic analysis, we also show that Epfn is controlled by WNT/b-CATENIN signaling in the limb ectoderm. Since the less severe phenotypes of the conditional removal of b-catenin in the limb ectoderm strongly resemble the limb phenotype of Epfn mutants, we propose that EPFN very likely functions as a modulator of WNT signaling in the limb ectoderm.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sp6 and Sp8 transcription factors control AER formation and dorsal-ventral patterning in limb development.PLoS Genet. 2014 Aug 28;10(8):e1004468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004468. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25166858 Free PMC article.
-
Smad1/Smad5 signaling in limb ectoderm functions redundantly and is required for interdigital programmed cell death.Dev Biol. 2012 Mar 1;363(1):247-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.037. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22240098 Free PMC article.
-
R-spondin2 expression in the apical ectodermal ridge is essential for outgrowth and patterning in mouse limb development.Dev Growth Differ. 2008 Feb;50(2):85-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2007.00978.x. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Dev Growth Differ. 2008. PMID: 18067586
-
Apical ectodermal ridge regulates three principal axes of the developing limb.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Oct.;21(10):757-766. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000285. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 33043642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Apical Ectodermal Ridge: morphological aspects and signaling pathways.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(7):857-71. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072416mf. Int J Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18956316 Review.
Cited by
-
Sp6 and Sp8 transcription factors control AER formation and dorsal-ventral patterning in limb development.PLoS Genet. 2014 Aug 28;10(8):e1004468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004468. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25166858 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical Wnt signaling and the regulation of divergent mesenchymal Fgf8 expression in axolotl limb development and regeneration.Elife. 2022 May 31;11:e79762. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79762. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35587651 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of cephalic fins in manta rays and their relatives: functional evidence for initiation of domain splitting and modulation of the Wnt signaling pathway in the pectoral fin AER of the little skate.Evodevo. 2024 Dec 27;15(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13227-024-00233-3. Evodevo. 2024. PMID: 39731200 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor/specificity protein evolution in the Spiralia and the implications for cephalopod visual system novelties.Proc Biol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;287(1937):20202055. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2020.2055. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Proc Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33081641 Free PMC article.
-
Novel genetic linkage of rat Sp6 mutation to Amelogenesis imperfecta.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012 Jun 7;7:34. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-34. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012. PMID: 22676574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamska M, MacDonald BT, Meisler MH. Doubleridge, a mouse mutant with defective compaction of the apical ectodermal ridge and normal dorsal-ventral patterning of the limb. Dev. Biol. 2003;255:350–362. - PubMed
-
- Ahn K, Mishina Y, Hanks MC, Behringer RR, Crenshaw EB., III BMPR-IA signaling is required for the formation of the apical ectodermal ridge and dorsal-ventral patterning of the limb. Development. 2001;128:4449–4461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

