Alterations in sympathetic neuroeffector transmission to mesenteric arteries but not veins in DOCA-salt hypertension
- PMID: 19914150
- PMCID: PMC2903739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2009.08.008
Alterations in sympathetic neuroeffector transmission to mesenteric arteries but not veins in DOCA-salt hypertension
Abstract
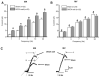
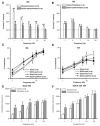
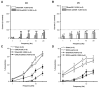
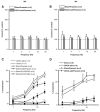
We studied hypertension-associated changes in prejunctional alpha(2) adrenergic receptor (alpha(2)-AR) function using amperometry to monitor in vitro norepinephrine (NE) measured as oxidation currents. Vasoconstriction was measured using video imaging. NE release was induced by electrical stimulation of sympathetic nerves associated with mesenteric arteries (MA) and veins (MV) of sham and DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. NE oxidation currents were larger in DOCA-salt compared to sham MA; there were no differences between currents in sham and DOCA-salt MV. Increases in NE oxidation currents followed a multi-exponential time course in sham MA. In DOCA-salt MA and sham and DOCA-salt MV, the time course was mono-exponential. Yohimbine (alpha(2)-AR antagonist, 1 microM), caused a mono-exponential increase in NE oxidation currents in sham and DOCA-salt MA. Yohimbine increased NE oxidation currents and constrictions more in sham compared to DOCA-salt MA and compared to MV. UK 14,304 (alpha(2)-AR agonist, 1.0 microM), reduced currents less in DOCA-salt MA and sham and DOCA-salt MV compared to sham MA. Prazosin (alpha(1)-AR antagonist, 0.1 microM) did not alter NE oxidation currents. Prazosin inhibited constrictions more in DOCA-salt compared to sham MA and almost completely blocked constrictions in sham and DOCA-salt MV. Prazosin-resistant constrictions in MA were blocked by the P2 receptor antagonist, PPADS (10 microM). Prejunctional alpha(2)-ARs modify NE concentrations near neuroeffector junctions in MA and MV. alpha(2)-AR function is most prominent in MA and is impaired in DOCA-salt MA but not MV. Purinergic transmission predominates in sham MA. NE is the dominant vasoconstrictor in DOCA-salt MA and sham and DOCA-salt MV.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impaired function of prejunctional adenosine A1 receptors expressed by perivascular sympathetic nerves in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Apr;345(1):32-40. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.199612. Epub 2013 Feb 8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23397055 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired function of alpha2-adrenergic autoreceptors on sympathetic nerves associated with mesenteric arteries and veins in DOCA-salt hypertension.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004 Apr;286(4):H1558-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00592.2003. Epub 2003 Dec 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14670814
-
Differential contributions of alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenoceptors to vasoconstriction in mesenteric arteries and veins of normal and hypertensive mice.Vascul Pharmacol. 2007 May;46(5):373-82. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Jan 27. Vascul Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17329171 Free PMC article.
-
Differential alterations in sympathetic neurotransmission in mesenteric arteries and veins in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Auton Neurosci. 2003 Feb 28;104(1):47-57. doi: 10.1016/S1566-0702(02)00287-4. Auton Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12559203
-
Antioxidant treatment restores prejunctional regulation of purinergic transmission in mesenteric arteries of deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats.Neuroscience. 2010 Jun 30;168(2):335-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.03.061. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20398741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Rat as a Model of Cardiovascular Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2010 Nov;6(4):291-7. doi: 10.2174/157340310793566109. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 22043205 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord injury alters purinergic neurotransmission to mesenteric arteries in rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):H223-H237. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00525.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31774690 Free PMC article.
-
Increased catecholamine secretion from single adrenal chromaffin cells in DOCA-salt hypertension is associated with potassium channel dysfunction.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Oct 16;4(10):1404-13. doi: 10.1021/cn400115v. Epub 2013 Aug 30. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23937098 Free PMC article.
-
Agmatine induced NO dependent rat mesenteric artery relaxation and its impairment in salt-sensitive hypertension.Nitric Oxide. 2013 Nov 30;35:65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Nitric Oxide. 2013. PMID: 23994446 Free PMC article.
-
Lesion of the OVLT markedly attenuates chronic DOCA-salt hypertension in rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):R568-R575. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00433.2017. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29897819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aalkjaer C, Heagerty AM, Petersen KK, Swales JD, Mulvany MJ. Evidence for increased media thickness, increased neuronal amine uptake, and depressed excitation–contraction coupling in isolated resistance vessels from essential hypertensives. Circ. Res. 1987;61:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Bobalova J, Mutafova-Yambolieva VN. Presynaptic alpha2-adrenoceptor-mediated modulation of adenosine 5′ triphosphate and noradrenaline corelease: differences in canine mesenteric artery and vein. J. Auton. Pharmacol. 2001;21:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Bouvier M, De Champlain J. Increased apparent norepinephrine release rate in anesthetized DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens., Part A Theory Pract. 1985;A7:1629–1645. - PubMed
-
- Bouvier M, de Champlain J. Increased basal and reactive plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine levels in awake DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1986;15:191–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

