Nuclear CDKs drive Smad transcriptional activation and turnover in BMP and TGF-beta pathways
- PMID: 19914168
- PMCID: PMC2818353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.035
Nuclear CDKs drive Smad transcriptional activation and turnover in BMP and TGF-beta pathways
Abstract
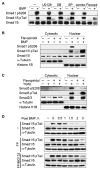
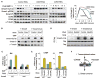
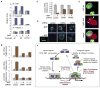
TGF-beta and BMP receptor kinases activate Smad transcription factors by C-terminal phosphorylation. We have identified a subsequent agonist-induced phosphorylation that plays a central dual role in Smad transcriptional activation and turnover. As receptor-activated Smads form transcriptional complexes, they are phosphorylated at an interdomain linker region by CDK8 and CDK9, which are components of transcriptional mediator and elongation complexes. These phosphorylations promote Smad transcriptional action, which in the case of Smad1 is mediated by the recruitment of YAP to the phosphorylated linker sites. An effector of the highly conserved Hippo organ size control pathway, YAP supports Smad1-dependent transcription and is required for BMP suppression of neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. The phosphorylated linker is ultimately recognized by specific ubiquitin ligases, leading to proteasome-mediated turnover of activated Smad proteins. Thus, nuclear CDK8/9 drive a cycle of Smad utilization and disposal that is an integral part of canonical BMP and TGF-beta pathways.
Figures




Comment in
-
Finale: the last minutes of Smads.Cell. 2009 Nov 13;139(4):658-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.038. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19914161
References
-
- Affolter M, Basler K. The Decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:663–674. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Blain SW, Massagué J. Different sensitivity of the transforming growth factor-beta cell cycle arrest pathway to c-Myc and MDM-2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:32066–32070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

