Context-dependent encoding in the human auditory brainstem relates to hearing speech in noise: implications for developmental dyslexia
- PMID: 19914180
- PMCID: PMC2778610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.006
Context-dependent encoding in the human auditory brainstem relates to hearing speech in noise: implications for developmental dyslexia
Abstract
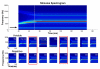
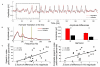
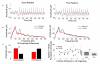
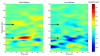
We examined context-dependent encoding of speech in children with and without developmental dyslexia by measuring auditory brainstem responses to a speech syllable presented in a repetitive or variable context. Typically developing children showed enhanced brainstem representation of features related to voice pitch in the repetitive context, relative to the variable context. In contrast, children with developmental dyslexia exhibited impairment in their ability to modify representation in predictable contexts. From a functional perspective, we found that the extent of context-dependent encoding in the auditory brainstem correlated positively with behavioral indices of speech perception in noise. The ability to sharpen representation of repeating elements is crucial to speech perception in noise, since it allows superior "tagging" of voice pitch, an important cue for segregating sound streams in background noise. The disruption of this mechanism contributes to a critical deficit in noise-exclusion, a hallmark symptom in developmental dyslexia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anatomical and behavioural correlates of auditory perception in developmental dyslexia.Brain. 2025 Mar 6;148(3):833-844. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae298. Brain. 2025. PMID: 39300826 Free PMC article.
-
Speech-perception-in-noise deficits in dyslexia.Dev Sci. 2009 Sep;12(5):732-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2009.00817.x. Dev Sci. 2009. PMID: 19702766
-
Using auditory-visual speech to probe the basis of noise-impaired consonant-vowel perception in dyslexia and auditory neuropathy.J Acoust Soc Am. 2005 Aug;118(2):1122-33. doi: 10.1121/1.1940509. J Acoust Soc Am. 2005. PMID: 16158666
-
Biological impact of music and software-based auditory training.J Commun Disord. 2012 Nov-Dec;45(6):403-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Commun Disord. 2012. PMID: 22789822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory-cognitive interaction in the neural encoding of speech in noise: a review.J Am Acad Audiol. 2010 Oct;21(9):575-85. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.21.9.3. J Am Acad Audiol. 2010. PMID: 21241645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involuntary monitoring of sound signals in noise is reflected in the human auditory evoked N1m response.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031634. Epub 2012 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22389671 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Speech-evoked auditory brainstem responses reflect familial and cognitive influences.Dev Sci. 2013 Jan;16(1):101-10. doi: 10.1111/desc.12009. Dev Sci. 2013. PMID: 23278931 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing it again and again: on-line subcortical plasticity in humans.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 26;5(10):e13645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013645. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21049035 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency Following Response and Speech Recognition Benefit for Combining a Cochlear Implant and Contralateral Hearing Aid.Trends Hear. 2020 Jan-Dec;24:2331216520902001. doi: 10.1177/2331216520902001. Trends Hear. 2020. PMID: 32003296 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Learning of Sound Categories in Dyslexia Is Associated with Reduced Regularity-Induced Auditory Cortex Adaptation.J Neurosci. 2022 Feb 16;42(7):1328-1342. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1533-21.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 30. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34969869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahissar M. Dyslexia and the anchoring-deficit hypothesis. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007;11(11):458–465. - PubMed
-
- Ahissar M, Lubin Y, Putter-Katz H, Banai K. Dyslexia and the failure to form a perceptual anchor. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9(12):1558–1564. - PubMed
-
- Bregman AS. Auditory scene analysis: The perceptual organization of sound. The MIT Press; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

