Laminar structure of spontaneous and sensory-evoked population activity in auditory cortex
- PMID: 19914188
- PMCID: PMC2778614
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.020
Laminar structure of spontaneous and sensory-evoked population activity in auditory cortex
Abstract
Spontaneous activity plays an important role in the function of neural circuits. Although many similarities between spontaneous and sensory-evoked neocortical activity have been reported, little is known about consistent differences between them. Here, using simultaneously recorded cortical populations and morphologically identified pyramidal cells, we compare the laminar structure of spontaneous and sensory-evoked population activity in rat auditory cortex. Spontaneous and evoked patterns both exhibited sparse, spatially localized activity in layer 2/3 pyramidal cells, with densely distributed activity in larger layer 5 pyramidal cells and putative interneurons. However, the propagation of spontaneous and evoked activity differed, with spontaneous activity spreading upward from deep layers and slowly across columns, but sensory responses initiating in presumptive thalamorecipient layers, spreading rapidly across columns. The similarity of sparseness patterns for both neural events and distinct spread of activity may reflect similarity of local processing and differences in the flow of information through cortical circuits, respectively.
Figures
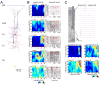
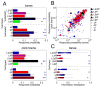

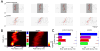
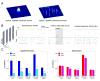


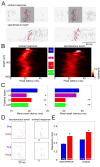
Comment in
-
Cortical dynamics by layers.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):298-300. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.024. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19914177
References
-
- Averbeck BB, Latham PE, Pouget A. Neural correlations, population coding and computation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Barlow HB. Single units and sensation: a neuron doctrine for perceptual psychology? Perception. 1972;1:371–394. - PubMed
-
- Barnes CA, McNaughton BL, Mizumori SJ, Leonard BW, Lin LH. Comparison of spatial and temporal characteristics of neuronal activity in sequential stages of hippocampal processing. Prog Brain Res. 1990;83:287–300. - PubMed
-
- Berger T, Borgdorff A, Crochet S, Neubauer FB, Lefort S, Fauvet B, Ferezou I, Carleton A, Luscher HR, Petersen CC. Combined voltage and calcium epifluorescence imaging in vitro and in vivo reveals subthreshold and suprathreshold dynamics of mouse barrel cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97:3751–3762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

