Psychophysiological biomarkers of workplace stressors
- PMID: 19914288
- PMCID: PMC2891393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.11.005
Psychophysiological biomarkers of workplace stressors
Abstract
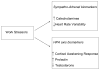
Workplace stressors are associated with greater coronary heart disease risk, although there is debate over the psychophysiological consequences of work stress. This study builds on recent reviews and examines the literature linking work stress with sympatho-adrenal biomarkers (plasma catecholamines and heart rate variability) and HPA axis biomarkers - the post-morning profile of cortisol.
Methods: Relevant studies using appropriate search terms were searched using the bibliographic databases PubMed, Embase, Biosys and Toxline. Four studies on plasma catecholamines, 10 studies on heart rate variability, and 16 studies on post-morning cortisol were reviewed.
Results: In the majority of studies that examined the association of HRV and work stress, greater reports of work stress is associated with lower heart rate variability. The findings for plasma catecholamines and cortisol secretion are less clear cut and suffer from poorer quality of studies in general.
Conclusion: There is evidence that work stress is related to elevated stress responses in terms of sympatho-adrenal and HPA axis biomarkers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypothalamo-pituitary adrenal axis and sympatho-adrenal medullary system responses to psychological stress were not attenuated in women with elevated physical fitness levels.Endocrine. 2016 Feb;51(2):369-79. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0687-6. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 26206752
-
Pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic nervous system responses to stress in women remitted from recurrent major depression.Psychosom Med. 2008 May;70(4):461-7. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31816b1aaa. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Psychosom Med. 2008. PMID: 18378864
-
Neuroendocrine and psychophysiologic responses in PTSD: a symptom provocation study.Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999 Jul;21(1):40-50. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00128-6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10379518 Clinical Trial.
-
Neuroendocrine coordination and youth behavior problems: A review of studies assessing sympathetic nervous system and hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis activity using salivary alpha amylase and salivary cortisol.Horm Behav. 2020 Jun;122:104750. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104750. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Horm Behav. 2020. PMID: 32302595 Review.
-
Function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system in models of acute stress in domestic farm animals.J Anim Sci. 1994 Jul;72(7):1891-8. doi: 10.2527/1994.7271891x. J Anim Sci. 1994. PMID: 7928769 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between work strain, need for recovery after work and cumulative cortisol among kindergarten teachers.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2015 Nov;88(8):1053-9. doi: 10.1007/s00420-015-1033-2. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2015. PMID: 25698458
-
Association between depressive symptoms and metabolic syndrome in police officers: results from two cross-sectional studies.J Environ Public Health. 2012;2012:861219. doi: 10.1155/2012/861219. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Environ Public Health. 2012. PMID: 22315628 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of emotional labor and cortisol concentration in hair among female kindergarten teachers.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2017 Jan;90(1):117-122. doi: 10.1007/s00420-016-1179-6. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2017. PMID: 27804039
-
The impact of sleep restriction while performing simulated physical firefighting work on cortisol and heart rate responses.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2016 Apr;89(3):461-75. doi: 10.1007/s00420-015-1085-3. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 26271391
-
Age, Daily Stress Processes, and Allostatic Load: A Longitudinal Study.J Aging Health. 2019 Oct;31(9):1671-1691. doi: 10.1177/0898264318788493. Epub 2018 Jul 18. J Aging Health. 2019. PMID: 30019595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appels A. Exhausted subjects, exhausted systems. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1997;640:153–154. - PubMed
-
- Bellingrath S, Kudielka BM. Effort-reward-imbalance and overcommitment are associated with hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis responses to acute psychosocial stress in healthy working schoolteachers. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2008;33:1335–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bellingrath S, Weigl T, Kudielka BM. Cortisol dysregulation in school teachers in relation to burnout, vital exhaustion, and effort-reward-imbalance. Biol Psychol. 2008;78:104–113. - PubMed
-
- Carney RM, Blumenthal JA, Stein PK, Watkins L, Catellier D, Berkman LF, Czajkowski SM, O’Connor C, Stone PH, Freedland KE. Depression, heart rate variability, and acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001;104:2024–2028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical