Advances in engineering of fluorescent proteins and photoactivatable proteins with red emission
- PMID: 19914857
- PMCID: PMC2819558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.10.011
Advances in engineering of fluorescent proteins and photoactivatable proteins with red emission
Abstract
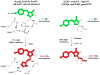
Monomeric fluorescent proteins of different colors are widely used to study behavior and targeting of proteins in living cells. Fluorescent proteins that irreversibly change their spectral properties in response to light irradiation of a specific wavelength, or photoactivate, have become increasingly popular to image intracellular dynamics and superresolution protein localization. Until recently, however, no optimized monomeric red fluorescent proteins and red photoactivatable proteins have been available. Furthermore, monomeric fluorescent proteins, which change emission from blue to red simply with time, so-called fluorescent timers, were developed to study protein age and turnover. Understanding of chemical mechanisms of the chromophore maturation or photoactivation into a red form will further advance engineering of fluorescent timers and photoactivatable proteins with enhanced and novel properties.
2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Matz MV, Fradkov AF, Labas YA, Savitsky AP, Zaraisky AG, Markelov ML, Lukyanov SA. Fluorescent proteins from nonbioluminescent Anthozoa species. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17:969–973. - PubMed
-
- Lukyanov KA, Chudakov DM, Lukyanov S, Verkhusha VV. Innovation: Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:885–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

