SHP-2 expression negatively regulates NK cell function
- PMID: 19915046
- PMCID: PMC2783243
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900088
SHP-2 expression negatively regulates NK cell function
Abstract
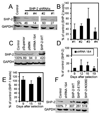
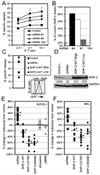
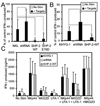
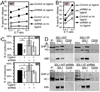
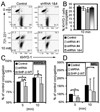
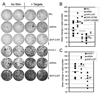
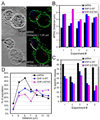
Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP-2) is required for full activation of Ras/ERK in many cytokine and growth factor receptor signaling pathways. In contrast, SHP-2 inhibits activation of human NK cells upon recruitment to killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIR). To determine how SHP-2 impacts NK cell activation in KIR-dependent or KIR-independent signaling pathways, we employed knockdown and overexpression strategies in NK-like cell lines and analyzed the consequences on functional responses. In response to stimulation with susceptible target cells, SHP-2-silenced NK cells had elevated cytolytic activity and IFN-gamma production, whereas cells overexpressing wild-type or gain-of-function mutants of SHP-2 exhibited dampened activities. Increased levels of SHP-2 expression over this range significantly suppressed microtubule organizing center polarization and granzyme B release in response to target cells. Interestingly, NK-target cell conjugation was only reduced by overexpressing SHP-2, but not potentiated in SHP-2-silenced cells, indicating that conjugation is not influenced by physiological levels of SHP-2 expression. KIR-dependent inhibition of cytotoxicity was unaffected by significant reductions in SHP-2 levels, presumably because KIR were still capable of recruiting the phosphatase under these limiting conditions. In contrast, the general suppressive effect of SHP-2 on cytotoxicity and cytokine release was much more sensitive to changes in cellular SHP-2 levels. In summary, our studies have identified a new, KIR-independent role for SHP-2 in dampening NK cell activation in response to tumor target cells in a concentration-dependent manner. This suppression of activation impacts microtubule organizing center-based cytoskeletal rearrangement and granule release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SHP-1- and phosphotyrosine-independent inhibitory signaling by a killer cell Ig-like receptor cytoplasmic domain in human NK cells.J Immunol. 2002 May 15;168(10):5047-57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.10.5047. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11994457
-
Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP-2) can play a direct role in the inhibitory function of killer cell Ig-like receptors in human NK cells.J Immunol. 2003 May 1;170(9):4539-47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.9.4539. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12707331
-
KIR2DL5 can inhibit human NK cell activation via recruitment of Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP-2).J Immunol. 2004 Jun 15;172(12):7385-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7385. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15187115
-
Inhibition of natural killer cell activation signals by killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (CD158).Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:223-33. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810119.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513144 Review.
-
Inhibitory receptor-mediated regulation of natural killer cells.Crit Rev Immunol. 2014;34(6):455-65. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2014012220. Crit Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25597309 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of intrinsic inhibitory checkpoints using nano-carriers to unleash NK cell activity.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Jan 11;14(1):e14073. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114073. Epub 2021 Nov 2. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34725941 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic KIR3DL3 expression modulates tissue-resident and innate-like T cells.Sci Immunol. 2023 Jun 30;8(84):eade5343. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ade5343. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Sci Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37390222 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Natural Killer Cells by Probiotics.For Immunopathol Dis Therap. 2016;7(1-2):41-55. doi: 10.1615/ForumImmunDisTher.2016017095. For Immunopathol Dis Therap. 2016. PMID: 28616355 Free PMC article.
-
SHP-1 phosphatase is a critical regulator in preventing natural killer cell self-killing.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044244. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952938 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Immune Checkpoint Therapy Resistance with SHP2 Inhibition in Cancer and Immune Cells: A Review of the Literature and Novel Combinatorial Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;15(22):5384. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225384. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biron CA. Activation and function of natural killer cell responses during viral infections. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:24–34. - PubMed
-
- MacFarlane AWt, Campbell KS. Signal transduction in natural killer cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;298:23–57. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Lanier LL. Natural killer cells and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2003;90:127–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

