Effects of metalloproteinase inhibition in a murine model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 19915515
- PMCID: PMC3366106
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181ca0aa2
Effects of metalloproteinase inhibition in a murine model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
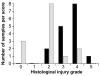
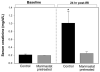
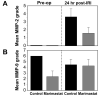
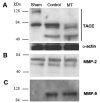
Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a leading cause of acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and delayed graft function in transplanted organs. Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) propagates the microinflammatory response that drives IRI. This study sought to determine the specific effects of Marimastat (Vernalis, BB-2516), a broad spectrum MMP and TNF-alpha-converting enzyme inhibitor, on IRI-induced ATN. Mice were pretreated with Marimastat or methylcellulose vehicle for 4 d before surgery. Renal pedicles were bilaterally occluded for 30 min and allowed to reperfuse for 24 h. Baseline creatinine levels were consistent between experimental groups; however, post-IRI creatinine levels were 4-fold higher in control mice (p < 0.0001). The mean difference between the post-IRI histology grades of Marimastat-treated and control kidneys was 1.57 (p = 0.003), demonstrating more severe damage to control kidneys. Post-IRI mean (+/-SEM) MMP-2 activity rose from baseline levels in control mice (3.62 +/- 0.99); however, pretreated mice presented only a slight increase in mean MMP-2 activity (1.57 +/- 0.72) (p < 0.001). In conclusion, these data demonstrate that MMP inhibition is associated with a reduction of IRI in a murine model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pretreatment with paricalcitol attenuates level and expression of matrix metalloproteinases in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury .Clin Nephrol. 2017 Nov;88(11):231-238. doi: 10.5414/CN109121. Clin Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28737133
-
Renal matrix metalloproteinase activity is unaffected by experimental ischemia-reperfusion injury and matrix metalloproteinase inhibition does not alter outcome of renal function.Exp Nephrol. 2001 Mar-Apr;9(2):118-24. doi: 10.1159/000052602. Exp Nephrol. 2001. PMID: 11150860
-
Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases reduces ischemia-reperfusion acute kidney injury.Lab Invest. 2011 Feb;91(2):170-80. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.174. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Lab Invest. 2011. PMID: 20956976
-
Broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibition curbs inflammation and liver injury but aggravates experimental liver fibrosis in mice.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 25;5(6):e11256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011256. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20593020 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological contributions of fucosyltransferases in renal ischemia reperfusion injury.J Immunol. 2002 Sep 1;169(5):2648-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.5.2648. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12193737
Cited by
-
Renoprotective Effect of Vardenafil and Avanafil in Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: Emerging Evidence from an Animal Model.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 22;12(5):670. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050670. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629096 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of matrix metalloproteinase-8 is associated with worsened recovery after ischemic kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2015 Apr;37(3):469-75. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2014.996842. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Ren Fail. 2015. PMID: 25578815 Free PMC article.
-
Gel Zymography for the Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in Aorta and Kidney Tissues.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2917:87-97. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4478-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40347334
-
Doxycycline Alters the Porcine Renal Proteome and Degradome during Hypothermic Machine Perfusion.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 23;44(2):559-577. doi: 10.3390/cimb44020039. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723325 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases as potential early biomarkers for renal fibrosis in children with nephrotic syndrome.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Feb;97(8):e9964. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009964. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29465592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shoskes DA, Halloran PF. Delayed graft function in renal transplantation: etiology, management and long-term significance. J Urol. 1996;155:1831–1840. - PubMed
-
- Paul LC. Chronic renal transplant loss. Kidney Int. 1995;47:1491–1499. - PubMed
-
- Azuma H, Nadeau K, Takada M, Mackenzie HS, Tilney NL. Cellular and molecular predictors of chronic renal dysfunction after initial ischemia/reperfusion injury of a single kidney. Transplantation. 1997;64:190–197. - PubMed
-
- Star RA. Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1998;54:1817–1831. - PubMed
-
- Kelly KJ, Molitoris BA. Acute renal failure in the new millennium: time to consider combination therapy. Semin Nephrol. 2000;20:4–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

