Common variants at five new loci associated with early-onset inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 19915574
- PMCID: PMC3267927
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.489
Common variants at five new loci associated with early-onset inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
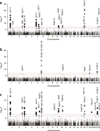
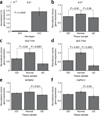
The inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are common causes of morbidity in children and young adults in the western world. Here we report the results of a genome-wide association study in early-onset IBD involving 3,426 affected individuals and 11,963 genetically matched controls recruited through international collaborations in Europe and North America, thereby extending the results from a previous study of 1,011 individuals with early-onset IBD. We have identified five new regions associated with early-onset IBD susceptibility, including 16p11 near the cytokine gene IL27 (rs8049439, P = 2.41 x 10(-9)), 22q12 (rs2412973, P = 1.55 x 10(-9)), 10q22 (rs1250550, P = 5.63 x 10(-9)), 2q37 (rs4676410, P = 3.64 x 10(-8)) and 19q13.11 (rs10500264, P = 4.26 x 10(-10)). Our scan also detected associations at 23 of 32 loci previously implicated in adult-onset Crohn's disease and at 8 of 17 loci implicated in adult-onset ulcerative colitis, highlighting the close pathogenetic relationship between early- and adult-onset IBD.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- M01 RR002172-26/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G0800675/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007762/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002172/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000064/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0600329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 DK007477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK069513/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00064/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK069513/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- 072789/Z/03/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0800759/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 DK060617/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/540/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- C06 RR011234/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

