Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 19915575
- PMCID: PMC2787725
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.487
Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson's disease
Abstract
We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in 1,713 individuals of European ancestry with Parkinson's disease (PD) and 3,978 controls. After replication in 3,361 cases and 4,573 controls, we observed two strong association signals, one in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein (SNCA; rs2736990, OR = 1.23, P = 2.24 x 10(-16)) and another at the MAPT locus (rs393152, OR = 0.77, P = 1.95 x 10(-16)). We exchanged data with colleagues performing a GWAS in Japanese PD cases. Association to PD at SNCA was replicated in the Japanese GWAS, confirming this as a major risk locus across populations. We replicated the effect of a new locus detected in the Japanese cohort (PARK16, rs823128, OR = 0.66, P = 7.29 x 10(-8)) and provide supporting evidence that common variation around LRRK2 modulates risk for PD (rs1491923, OR = 1.14, P = 1.55 x 10(-5)). These data demonstrate an unequivocal role for common genetic variants in the etiology of typical PD and suggest population-specific genetic heterogeneity in this disease.
Figures
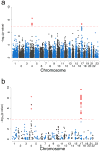
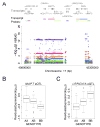
Comment in
-
Evidence for a common pathway linking neurodegenerative diseases.Nat Genet. 2009 Dec;41(12):1261-2. doi: 10.1038/ng1209-1261. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19935760 No abstract available.
References
-
- Toda T. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nature Genetics. 2009 in press. - PubMed
-
- Fung HC, et al. Genome-wide genotyping in Parkinson’s disease and neurologically normal controls: first stage analysis and public release of data. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:911–6. - PubMed
-
- Maraganore DM, et al. Collaborative analysis of alpha-synuclein gene promoter variability and Parkinson disease. Jama. 2006;296:661–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- J-0804/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 AG000949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 ES101986/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041509/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G-0909/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- R01 NS050425/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058714/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400000/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G108/638/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

