Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are therapeutic for Staphylococcus aureus abscesses in a murine model of infection
- PMID: 19915659
- PMCID: PMC2771897
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007804
Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are therapeutic for Staphylococcus aureus abscesses in a murine model of infection
Abstract
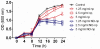
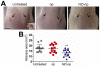
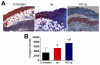
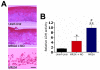
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is a leading cause of a diverse spectrum of bacterial diseases, including abscesses. Nitric oxide (NO) is a critical component of the natural host defense against pathogens such as SA, but its therapeutic applications have been limited by a lack of effective delivery options. We tested the efficacy of a NO-releasing nanoparticle system (NO-np) in methicillin-resistant SA (MRSA) abscesses in mice. The results show that the NO-np exert antimicrobial activity against MRSA in vitro and in abscesses. Topical or intradermal NO-np treatment of abscesses reduces the involved area and bacterial load while improving skin architecture. Notably, we evaluated pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines that are involved in immunomodulation and wound healing, revealing that NO-np lead to a reduction in angiogenesis preventing bacterial dissemination from abscesses. These data suggest that NO-np may be useful therapeutics for microbial abscesses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Noskin GA, Rubin RJ, Schentag JJ, Kluytmans J, Hedblom EC, et al. National trends in Staphylococcus aureus infection rates: impact on economic burden and mortality over a 6-year period (1998-2003). Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:1132–1140. - PubMed
-
- Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, et al. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:666–674. - PubMed
-
- Hiramatsu K, Hanaki H, Ino T, Yabuta K, Oguri T, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strain with reduced vancomycin susceptibility. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997;40:135–136. - PubMed
-
- Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:1763–1771. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

