The effect of bone marrow aspiration strategy on the yield and quality of human mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 19916699
- PMCID: PMC2823327
- DOI: 10.3109/17453670903278241
The effect of bone marrow aspiration strategy on the yield and quality of human mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
Introduction: Large inter-donor differences exist in human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) yield and the response of these cells to osteogenic stimuli. The source of these differences may be clinical differences in stem cell characteristics between individuals or the aspiration procedure itself.
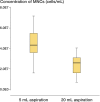
Methods: From a total of 23 donors, we aimed to take 2 consecutive 10-mL aspirates from the same site in 17 donors and in 6 donors we aimed to take a 5-mL and a 20-mL aspirate. The aspiration was stopped either when the syringe was full or when no more bone marrow came through. Mononuclear cell yield (MNC), MSC yield, and differentiation capacity were analyzed for intra-donor and inter-donor variation. We analyzed the effect of the dilution with peripheral blood by drawing 20 mL at once.
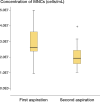
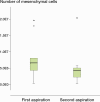
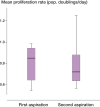
Results: There was a high correlation between the first and second aspiration volumes, and aspirates with a volume of less than 8 mL showed a large variation in cellular yield. The second 10-mL aspirate, and also 20-mL aspirates, contained a lower concentration of nucleated cells and yielded lower numbers of mesenchymal stem cells. No effect of the aspiration procedure on the biological characteristics of the mesenchymal stem cells was seen.
Conclusion: We recommend collection volumes of bone marrow aspirates of at least 8 mL to reduce the risk of obtaining aspirates with low cell numbers. From the same site, a second aspiration or an aspirate of > 10 mL can be drawn without any loss of biological quality due to dilution with peripheral blood.
Figures


References
-
- Bianco P, Robey PG. Stem cells in tissue engineering. Nature. 2001;414((6859)):118–21. - PubMed
-
- Brandao-Burch A, Utting J, Orriss I, Arnett T. Acidosis inhibits bone formation by osteoblasts in vitro by preventing mineralization. Calcif Tissue Int. 2005;77((3)):167–74. - PubMed
-
- Caplan A. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9((5)):641–50. - PubMed
-
- de Boer J, Siddappa R, Gaspar C, van Apeldoorn A, Fodde R, van Blitterswijk C. Wnt signaling inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 2004;34((5)):818–26. - PubMed
-
- de Bruijn JD, van den Brink I, Mendes S, Dekker R, Bovell YP, van Blitterswijk CA. Bone induction by implants coated with cultured osteogenic bone marrow cells. Adv Dent Res. 1999;13((1)):74–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
