3' tag digital gene expression profiling of human brain and universal reference RNA using Illumina Genome Analyzer
- PMID: 19917133
- PMCID: PMC2781828
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-531
3' tag digital gene expression profiling of human brain and universal reference RNA using Illumina Genome Analyzer
Abstract
Background: Massive parallel sequencing has the potential to replace microarrays as the method for transcriptome profiling. Currently there are two protocols: full-length RNA sequencing (RNA-SEQ) and 3'-tag digital gene expression (DGE). In this preliminary effort, we evaluated the 3' DGE approach using two reference RNA samples from the MicroArray Quality Control Consortium (MAQC).
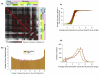
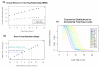
Results: Using Brain RNA sample from multiple runs, we demonstrated that the transcript profiles from 3' DGE were highly reproducible between technical and biological replicates from libraries constructed by the same lab and even by different labs, and between two generations of Illumina's Genome Analyzers. Approximately 65% of all sequence reads mapped to mitochondrial genes, ribosomal RNAs, and canonical transcripts. The expression profiles of brain RNA and universal human reference RNA were compared which demonstrated that DGE was also highly quantitative with excellent correlation of differential expression with quantitative real-time PCR. Furthermore, one lane of 3' DGE sequencing, using the current sequencing chemistry and image processing software, had wider dynamic range for transcriptome profiling and was able to detect lower expressed genes which are normally below the detection threshold of microarrays.
Conclusion: 3' tag DGE profiling with massive parallel sequencing achieved high sensitivity and reproducibility for transcriptome profiling. Although it lacks the ability of detecting alternative splicing events compared to RNA-SEQ, it is much more affordable and clearly out-performed microarrays (Affymetrix) in detecting lower abundant transcripts.
Figures
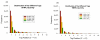


References
-
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, Fuldner RA, Bult CJ, Lee NH, Kirkness EF, Weinstock KG, Gocayne JD, White O, Sutton G, Blake JA, Brandon RC, Chiu M, Clayton RA, Cline RT, Cotton MD, Hughes JE, Fine LD, Fitzgerald LM, FitzHugh WM, Fritchman JL, Geoghagen NSM, Glodek A, Gnehm CL, Hanna MC, Hedblom E, Hinkle PS Jr, Kelley JM, Klimek KM, Kelley JC, Liu L, Marmaros SM, Merrick JM, Moreno-Palanques RF, McDonald LA, Nguyen DT, Pellegrino SM, Phillips CA, Ryder SE, Scott JL, Saudek DM, Shirley R, Small KV, Spriggs TA, Utterback TR, Weidman JF, Li Y, Barthlow R, Bednarik DP, Cao L, Cepeda MA, Coleman TA, Collins E, Dimke D, Feng P, Ferrie A, Fischer C, Hastings GA, He W, Hu J, Huddleston KA, Greene JM, Gruber J, Hudson P, Kim A, Kozak DL, Kunsch C, Ji H, Li H, Meissner PS, Olsen H, Raymond L, Wei Y, Wing J, Xu C, Yu G, Ruben SM, Dillon PJ, Fannon MR, Rosen CA, Haseltine WA, Fields C, M FC, Venter JC. Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. Nature. 1995;377(6547 Suppl):3–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

