High-chloride concentrations abolish the binding of adenine nucleotides in the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier family
- PMID: 19917217
- PMCID: PMC2776247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.08.047
High-chloride concentrations abolish the binding of adenine nucleotides in the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier family
Abstract
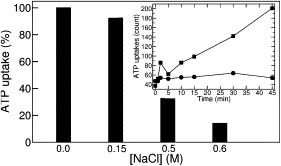
The ADP/ATP carrier (AAC) is a very effective membrane protein that mediates the exchange of ADP and ATP across the mitochondrial membrane. In vivo transport measurements on the AAC overexpressed in Escherichia coli demonstrate that this process can be severely inhibited by high-chloride concentrations. Molecular-dynamics simulations reveal a strong modification of the topology of the local electric field related to the number of chloride ions inside the cavity. Halide ions are shown to shield the positive charges lining the internal cavity of the carrier by accurate targeting of key basic residues. These specific amino acids are highly conserved as highlighted by the analysis of multiple AAC sequences. These results strongly suggest that the chloride concentration acts as an electrostatic lock for the mitochondrial AAC family, thereby preventing adenine nucleotides from reaching their dedicated binding sites.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The ADP and ATP transport in mitochondria and its carrier.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1778(10):1978-2021. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.04.011. Epub 2008 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18510943 Review.
-
Binding of ADP in the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier is driven by an electrostatic funnel.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Sep 24;130(38):12725-33. doi: 10.1021/ja8033087. Epub 2008 Aug 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18729359
-
Molecular dynamics simulations on apo ADP/ATP carrier shed new lights on the featured motif of the mitochondrial carriers.Mitochondrion. 2019 Jul;47:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 23. Mitochondrion. 2019. PMID: 31129042
-
Two residues of a conserved aromatic ladder of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier are crucial to nucleotide transport.Biochemistry. 2008 Dec 16;47(50):13223-31. doi: 10.1021/bi8012565. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 19086155
-
[Structural and functional properties of the C-terminal region of mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Feb;130(2):199-204. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.199. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20118643 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of thiamine pyrophosphate import into mitochondria: a molecular simulation study.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Sep;35(9):987-1007. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00414-5. Epub 2021 Aug 18. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 34406552
-
The effect of respiration buffer composition on mitochondrial metabolism and function.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 1;12(11):e0187523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187523. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29091971 Free PMC article.
-
ANT1 Activation and Inhibition Patterns Support the Fatty Acid Cycling Mechanism for Proton Transport.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 2;22(5):2490. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052490. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801254 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping multiple potential ATP binding sites on the matrix side of the bovine ADP/ATP carrier by the combined use of MD simulation and docking.J Mol Model. 2012 Jun;18(6):2377-86. doi: 10.1007/s00894-011-1255-5. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Mol Model. 2012. PMID: 21989959
-
Dynamics of SLC25A51 reveal preference for oxidized NAD+ and substrate led transport.EMBO Rep. 2023 Oct 9;24(10):e56596. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256596. Epub 2023 Aug 14. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37575034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dahout-Gonzalez C., Nury H., Trézéguet V., Lauquin G.J.-M., Pebay-Peyroula E. Molecular, functional, and pathological aspects of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006;21:242–249. - PubMed
-
- Reference deleted in proof.
-
- Reference deleted in proof.
-
- Reference deleted in proof.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

