Overgeneralization of conditioned fear as a pathogenic marker of panic disorder
- PMID: 19917595
- PMCID: PMC2806514
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09030410
Overgeneralization of conditioned fear as a pathogenic marker of panic disorder
Erratum in
- Am J Psychiatry. 2010 Jan;167(1):106
Abstract
Objective: Classical conditioning features prominently in many etiological accounts of panic disorder. According to such accounts, neutral conditioned stimuli present during panic attacks acquire panicogenic properties. Conditioned stimuli triggering panic symptoms are not limited to the original conditioned stimuli but are thought to generalize to stimuli resembling those co-occurring with panic, resulting in the proliferation of panic cues. The authors conducted a laboratory-based assessment of this potential correlate of panic disorder by testing the degree to which panic patients and healthy subjects manifest generalization of conditioned fear.
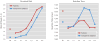
Method: Nineteen patients with a DSM-IV-TR diagnosis of panic disorder and 19 healthy comparison subjects were recruited for the study. The fear-generalization paradigm consisted of 10 rings of graded size presented on a computer monitor; one extreme size was a conditioned danger cue, the other extreme a conditioned safety cue, and the eight rings of intermediary size created a continuum of similarity from one extreme to the other. Generalization was assessed by conditioned fear potentiating of the startle blink reflex as measured with electromyography (EMG).
Results: Panic patients displayed stronger conditioned generalization than comparison subjects, as reflected by startle EMG. Conditioned fear in panic patients generalized to rings with up to three units of dissimilarity to the conditioned danger cue, whereas generalization in comparison subjects was restricted to rings with only one unit of dissimilarity.
Conclusions: The findings demonstrate a marked proclivity toward fear overgeneralization in panic disorder and provide a methodology for laboratory-based investigations of this central, yet understudied, conditioning correlate of panic. Given the putative molecular basis of fear conditioning, these results may have implications for novel treatments and prevention in panic disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bouton ME, Mineka S, Barlow DH. A modern learning theory perspective on the etiology of panic disorder. Psychol Rev. 2001;108:4–32. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein AJ, Chambless DL. A reanalysis of agoraphobia. Behav Ther. 1978;9:47–59.
-
- Wolpe J, Rowan VC. Panic disorder: a product of classical conditioning. Behav Res Ther. 1988;26:441–450. - PubMed
-
- Eysenck HJ, Rachman S. The Causes and Cures of Neurosis. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul; 1965.
-
- Razran G. The observable unconscious and the inferable conscious in current Soviet psychophysiology: interoceptive conditioning, semantic conditioning, and the orienting reflex. Psychol Rev. 1961;68:81–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

