Epidermal loss of JunB leads to a SLE phenotype due to hyper IL-6 signaling
- PMID: 19918056
- PMCID: PMC2787143
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910371106
Epidermal loss of JunB leads to a SLE phenotype due to hyper IL-6 signaling
Abstract
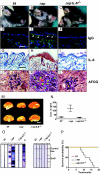
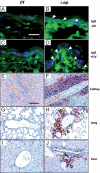
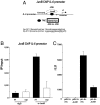
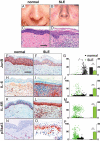
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease affecting various tissues. Involvement of B and T cells as well as increased cytokine levels have been associated with disease manifestation. Recently, we demonstrated that mice with epidermal loss of JunB (JunB(Deltaep)) develop a myeloproliferative syndrome (MPS) due to high levels of G-CSF which are secreted by JunB-deficient keratinocytes. In addition, we show that JunB(Deltaep) mice develop a SLE phenotype linked to increased epidermal interleukin 6 (IL-6) secretion. Intercrosses with IL-6-deficient mice could rescue the SLE phenotype. Furthermore, we show that JunB binds to the IL-6 promoter and transcriptionally suppresses IL-6. Facial skin biopsies of human SLE patients similarly revealed low JunB protein expression and high IL-6, activated Stat3, Socs-1, and Socs-3 levels within lupus lesions. Thus, keratinocyte-induced IL-6 secretion can cause SLE and systemic autoimmunity. Our results support trials to use alpha-IL-6 receptor antibody therapy for treatment of SLE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6: From basic science to medicine—40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T. Interleukin 6 and its receptor: Ten years later. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16:249–284. - PubMed
-
- Youinou P, Jamin C. The weight of interleukin-6 in B cell-related autoimmune disorders. J Autoimmun. 2009;32:206–210. - PubMed
-
- Eitner F, et al. Role of interleukin-6 in mediating mesangial cell proliferation and matrix production in vivo. Kidney Int. 1997;51:69–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

