GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor antagonists prevent Abeta-mediated synaptic plasticity disruption in vivo
- PMID: 19918059
- PMCID: PMC2787128
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908083106
GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor antagonists prevent Abeta-mediated synaptic plasticity disruption in vivo
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 13;107(28):12734. Anwy, Roger [corrected to Anwyl, Roger]
Abstract
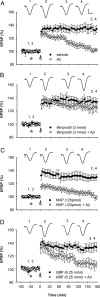
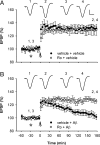
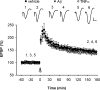
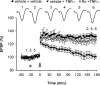
Currently, treatment with the relatively low-affinity NMDA receptor antagonist memantine provides limited benefit in Alzheimer's disease (AD). One probable dose-limiting factor in the use of memantine is the inhibition of NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity mechanisms believed to underlie certain forms of memory. Moreover, amyloid-beta protein (Abeta) oligomers that are implicated in causing the cognitive deficits of AD potently inhibit this form of plasticity. Here we examined if subtype-preferring NMDA receptor antagonists could preferentially protect against the inhibition of NMDA receptor-dependent plasticity of excitatory synaptic transmission by Abeta in the hippocampus in vivo. Using doses that did not affect control plasticity, antagonists selective for NMDA receptors containing GluN2B but not other GluN2 subunits prevented Abeta(1-42) -mediated inhibition of plasticity. Evidence that the proinflammatory cytokine TNFalpha mediates this deleterious action of Ass was provided by the ability of TNFalpha antagonists to prevent Abeta(1-42) inhibition of plasticity and the abrogation of a similar disruptive effect of TNFalpha using a GluN2B-selective antagonist. Moreover, at nearby synapses that were resistant to the inhibitory effect of TNFalpha, Abeta(1-42) did not significantly affect plasticity. These findings suggest that preferentially targeting GluN2B subunit-containing NMDARs may provide an effective means of preventing cognitive deficits in early Alzheimer's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
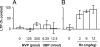
References
-
- Hynd MR, Scott HL, Dodd PR. Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Int. 2004;45:583–595. - PubMed
-
- Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: Lessons from the Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Raina P, et al. Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating dementia: Evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:379–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

