A structural basis for H-NOX signaling in Shewanella oneidensis by trapping a histidine kinase inhibitory conformation
- PMID: 19918063
- PMCID: PMC2785238
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911645106
A structural basis for H-NOX signaling in Shewanella oneidensis by trapping a histidine kinase inhibitory conformation
Abstract
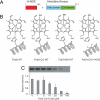
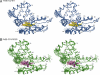
Heme nitric oxide/oxygen (H-NOX) proteins are found in eukaryotes where they are typically part of a larger protein such as soluble guanylate cyclase and in prokaryotes where they are often found in operons with a histidine kinase, suggesting that H-NOX proteins serve as sensors for NO and O(2) in signaling pathways. The Fe(II)-NO complex of the H-NOX protein from Shewanella oneidensis inhibits the autophosphorylation of the operon-associated histidine kinase, whereas the ligand-free H-NOX has no effect on the kinase. NMR spectroscopy was used to determine the structures of the Fe(II)-CO complex of the S. oneidensis H-NOX and the Fe(II)-CO complex of the H103G H-NOX mutant as a mimic of the ligand-free and kinase-inhibitory Fe(II)-NO H-NOX, respectively. The results provide a molecular glimpse into the ligand-induced conformational changes that may underlie kinase inhibition and the subsequent control of downstream signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Derbyshire ER, Marletta MA. Biochemistry of soluble guanylate cyclase. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Chan MK. Recent advances in heme-protein sensors. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001;5:216–222. - PubMed
-
- Boon EM, Huang SH, Marletta MA. A molecular basis for NO selectivity in soluble guanylate cyclase. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:53–59. - PubMed
-
- Huang SH, Rio DC, Marletta MA. Ligand binding and inhibition of an oxygen-sensitive soluble guanylate cyclase, Gyc-88E, from Drosophila. Biochemistry. 2007;46:15115–15122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

