CSF concentrations of brain tryptophan and kynurenines during immune stimulation with IFN-alpha: relationship to CNS immune responses and depression
- PMID: 19918244
- PMCID: PMC2844942
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2009.116
CSF concentrations of brain tryptophan and kynurenines during immune stimulation with IFN-alpha: relationship to CNS immune responses and depression
Abstract
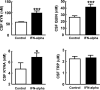
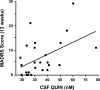
Cytokine-induced activation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) catabolizes L-tryptophan (TRP) into L-kynurenine (KYN), which is metabolized to quinolinic acid (QUIN) and kynurenic acid (KA). QUIN and KA are neuroactive and may contribute to the behavioral changes experienced by some patients during exposure to inflammatory stimuli such as interferon (IFN)-alpha. A relationship between depressive symptoms and peripheral blood TRP, KYN and KA during treatment with IFN-alpha has been described. However, whether peripheral blood changes in these IDO catabolites are manifest in the brain and whether they are related to central nervous system cytokine responses and/or behavior is unknown. Accordingly, TRP, KYN, QUIN and KA were measured in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood along with CSF concentrations of relevant cytokines, chemokines and soluble cytokine receptors in 27 patients with hepatitis C after approximately 12 weeks of either treatment with IFN-alpha (n=16) or no treatment (n=11). Depressive symptoms were assessed using the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale. IFN-alpha significantly increased peripheral blood KYN, which was accompanied by marked increases in CSF KYN. Increased CSF KYN was in turn associated with significant increases in CSF QUIN and KA. Despite significant decreases in peripheral blood TRP, IFN-alpha had no effect on CSF TRP concentrations. Increases in CSF KYN and QUIN were correlated with increased CSF IFN-alpha, soluble tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor 2 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 as well as increased depressive symptoms. In conclusion, peripheral administration of IFN-alpha activated IDO in concert with central cytokine responses, resulting in increased brain KYN and QUIN, which correlated with depressive symptoms.
Figures

References
-
- Anisman H, Merali Z, Hayley S. Neurotransmitter, peptide and cytokine processes in relation to depressive disorder: comorbidity between depression and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 2008;85:1–74. - PubMed
-
- Yirmiya R. Endotoxin produces a depressive-like episode in rats. Brain Res. 1996;711:163–174. - PubMed
-
- Zorrilla EP, Luborsky L, McKay JR, Rosenthal R, Houldin A, Tax A, et al. The relationship of depression and stressors to immunological assays: a meta-analytic review. Brain Behav Immun. 2001;15:199–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR0039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH064619/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 079829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083746/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG029573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH070553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073921/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071349/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 71349/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K05 MH069124/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG 029573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

