HMGB1, an innate alarmin, in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 19918326
- PMCID: PMC2776260
HMGB1, an innate alarmin, in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes
Abstract
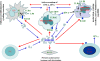
HMGB1, an evolutionarily conserved chromosomal protein, was recently re-discovered to act as a "danger signal" (alarmin) to alert the innate immune system for the initiation of host defense or tissue repair. Extracellular HMGB1 can be either passively released from damaged/necrotic cells or secreted by activated immune cells. Upon stimulation, dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells secrete high levels of HMGB1 into the intercellular milieu. HMGB1 is potent to target DCs, macrophages, neutrophils and CD4(+) T cells. It also upregulates the expression of BCL-XL by which it may prevent the elimination of activated immune cells. As a result, HMGB1 has been suggested to be implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). Given the similarities of autoimmune response against beta cell self-antigens in type 1 diabetes (T1D), in this view we will discuss the possible implications of HMGB1 in T1D pathogenesis. Specifically, we will summarize and update the advancement of HMGB1 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune initiation and progression during T1D development, as well as islet allograft rejection of diabetic patients after islet transplantation. Elucidation of the role for HMGB1 in T1D pathogenesis would not only enhance the understanding of disease etiology, but also have the potential to shed new insight into the development of therapeutic strategies for prevention or intervention of this disorder.
Keywords: HMGB1; innate alarmin; pathogenesis type 1 diabetes; review.
Figures

References
-
- Wang CY, Podolsky R, She JX. Genetic and functional evidence supporting SUMO4 as a type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1079:257–267. - PubMed
-
- Wang CY, She JX. SUMO4 and its role in type 1 diabetes pathogenesis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Guo D, Isales CM, Eizirik DL, Atkinson M, She JX, Wang CY. SUMO wrestling with type 1 diabetes. J Mol Med. 2005;83:504–513. - PubMed
-
- Wang CY, Han J, She JX. World Scientific, editor. Genetic factors for human type 1 diabetes. Current Topics in Human Genetics (Studies in Complex Diseases) 2008;24:693–727.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
