Plugs clog the glandular outlets in fundic gland polyps
- PMID: 19918330
- PMCID: PMC2776267
Plugs clog the glandular outlets in fundic gland polyps
Abstract
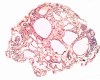
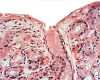
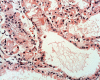
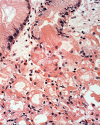
A systematic histologic analysis of 62 gastric fundic gland polyps (FGP) was carried out. All FGP (100%) showed foveolar cells with hypertrophic cytoplasm. In 95% of the FGP, parietal cells ballooned into the lumen and in 93%, exfoliated anucleated structures with eosinophilic granules were found. Plugs of anucleated structures with eosinophilic granules, most likely derived from exfoliated parietal cells, were found to clog the outlets of the glands in 86% of the FGP. None of the 30 control gastric biopsies without FGP had similar cellular aberrations. FGP seems to evolve by cellular aberrations affecting parietal cells. This is not surprising considering that genetic mutations are recorded in FGP with a common APC/b-catenin pathway in both FAP and sporadic cases. The genetic mutations in FGP might alter the biological behavior of the parietal cells, leading to increased exfoliation with clogging of the outlets of the glands. Thus, the blocking of the glandular outflow by plugs of anucleated structures with eosinophilic granules is the most likely cause for the cystic accumulation of "normal" glandular secretions.
Keywords: Fundic gland polyps; cystic formations; eosinophilic plugs.
Figures


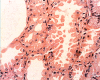

Similar articles
-
Gastric fundic gland polyps in south-east Scotland: absence of adenomatous polyposis coli gene mutations and a strikingly low prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Nov;17(11):1161-4. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02863.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 12453274
-
Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection and mucosal atrophy on gastric lesions in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis.Gut. 2002 Oct;51(4):485-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.51.4.485. Gut. 2002. PMID: 12235068 Free PMC article.
-
[Sporadic fundic gland polyposis--a case study].Ugeskr Laeger. 2007 Sep 24;169(39):3304-5. Ugeskr Laeger. 2007. PMID: 17953893 Danish.
-
High-grade dysplasia in sporadic fundic gland polyps: clinically relevant or not?Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003 Nov;15(11):1153-6. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200311000-00001. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003. PMID: 14560146 Review.
-
Fundic gland polyps: a still elusive entity on the eve of the year 2000.Pol J Pathol. 2000;51(1):3-8. Pol J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10833897 Review.
Cited by
-
The Natural Antimicrobial Enzyme Lysozyme is Up-Regulated in Gastrointestinal Inflammatory Conditions.Pathogens. 2014 Jan 16;3(1):73-92. doi: 10.3390/pathogens3010073. Pathogens. 2014. PMID: 25437608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nishiura M, Hirota T, Itabashi M. A clinical and histopathological study of gastric polyps in familial polyposis coli. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984;79:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Lee RG, Burt RW. The histopathology of fundic gland polyps of the stomach. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986;86:498–503. - PubMed
-
- Elster K. Histologic classification of gastric polyps. Curr Top Pathol. 1976;63:77–93. - PubMed
-
- Lee RG, Burt RW. The histopathology of fundic gland polyps of the stomach. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986;86:498–503. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
