Multiyear climate variability and dengue--El Niño southern oscillation, weather, and dengue incidence in Puerto Rico, Mexico, and Thailand: a longitudinal data analysis
- PMID: 19918363
- PMCID: PMC2771282
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000168
Multiyear climate variability and dengue--El Niño southern oscillation, weather, and dengue incidence in Puerto Rico, Mexico, and Thailand: a longitudinal data analysis
Abstract
Background: The mosquito-borne dengue viruses are a major public health problem throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Changes in temperature and precipitation have well-defined roles in the transmission cycle and may thus play a role in changing incidence levels. The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a multiyear climate driver of local temperature and precipitation worldwide. Previous studies have reported varying degrees of association between ENSO and dengue incidence.
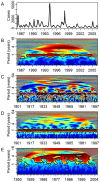
Methods and findings: We analyzed the relationship between ENSO, local weather, and dengue incidence in Puerto Rico, Mexico, and Thailand using wavelet analysis to identify time- and frequency-specific association. In Puerto Rico, ENSO was transiently associated with temperature and dengue incidence on multiyear scales. However, only local precipitation and not temperature was associated with dengue on multiyear scales. In Thailand, ENSO was associated with both temperature and precipitation. Although precipitation was associated with dengue incidence, the association was nonstationary and likely spurious. In Mexico, no association between any of the variables was observed on the multiyear scale.
Conclusions: The evidence for a relationship between ENSO, climate, and dengue incidence presented here is weak. While multiyear climate variability may play a role in endemic interannual dengue dynamics, we did not find evidence of a strong, consistent relationship in any of the study areas. The role of ENSO may be obscured by local climate heterogeneity, insufficient data, randomly coincident outbreaks, and other, potentially stronger, intrinsic factors regulating transmission dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Comment in
-
The link between dengue incidence and El Niño southern oscillation.PLoS Med. 2009 Nov;6(11):e1000185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000185. Epub 2009 Nov 17. PLoS Med. 2009. PMID: 19918362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gubler DJ. Dengue/dengue haemorrhagic fever: history and current status. Novartis Found Symp. 2006;277:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Halstead SB. Dengue virus-mosquito interactions. Annu Rev Entomol. 2008;53:273–291. - PubMed
-
- Christophers SR. Cambridge: The University Press; 1960. Aedes aegypti (L.): the yellow fever mosquito.
-
- Focks DA, Haile DG, Daniels E, Mount GA. Dynamic life table model for Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae): analysis of the literature and model development. J Med Entomol. 1993;30:1003–1017. - PubMed
-
- Keirans JE, Fay RW. Effect of food and temperature on Aedes aegypti (L.) and Aedes triseriatus (Say) larval development. Mosq News. 1968;28:338–341.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

