Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in circulating tumor cells of breast cancer patients
- PMID: 19919679
- PMCID: PMC2815547
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2452
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in circulating tumor cells of breast cancer patients
Abstract
Introduction: The detection of peripheral blood circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and bone marrow disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) in breast cancer patients is associated with a high incidence of disease relapse and disease-related death. Since hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) play an important role in angiogenesis and tumor progression, the purpose of the current study was to investigate their expression in CTCs.
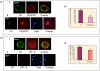
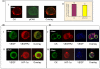
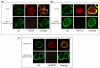
Methods: The expression of cytokeratins (CK), VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGF2), HIF-1alpha and phosphorylated-focal adhesion kinase (pFAK) in CTCs from 34 patients with metastatic breast cancer who had detectable CK-19 mRNA-positive CTCs was assessed using double staining experiments and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were stained with a monoclonal A45-B/B3 pancytokeratin antibody in combination with either VEGF or VEGFR2 or HIF-1alpha or pFAK antibodies, respectively.
Results: pFAK expression in circulating tumor cells was detected in 92% of patients whereas expression of VEGF, VEGF2 and HIF-1alpha was observed in 62%, 47% and 76% of patients, respectively. VEGF, VEGF2, HIF-1alpha and pFAK were expressed in 73%, 71%, 56% and 81%, respectively, of all the detected CTCs. Vascular endothelial growth mRNA was also detected by quantitative real-time RT-PCR in immunomagnetically-separated CTCs. Double and triple staining experiments in cytospins of immunomagnetically-isolated CTCs showed that VEGF co-expressed with HIF-1alpha and VEGF2.
Conclusions: The expression of pFAK, HIF-1alpha, VEGF and VEGF2 in CTCs of patients with metastatic breast cancer could explain the metastatic potential of these cells and may provide a therapeutic target for their elimination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GPER mediates the angiocrine actions induced by IGF1 through the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in the breast tumor microenvironment.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 6;19(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0923-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29212519 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of silencing HIF-1alpha by RNA interference on expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in osteosarcoma cell line SaOS-2 under hypoxia].Ai Zheng. 2005 May;24(5):531-5. Ai Zheng. 2005. PMID: 15890092 Chinese.
-
The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 1;62(17):5089-95. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12208766
-
HIF-1α, VEGF and WT-1 are protagonists in bilateral primary angiosarcoma of breast: a case report and review of literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(3):247-53. Epub 2012 Mar 25. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22558480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis induction in breast cancer: A paracrine paradigm.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021 Oct;39(7):860-873. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3663. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021. PMID: 34505714 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer-stromal cell interactions mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis.Oncogene. 2013 Aug 29;32(35):4057-63. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.578. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23222717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
More precise prediction in Chinese patients with penile squamous cell carcinoma: protein kinase CK2α catalytic subunit (CK2α) as a poor prognosticator.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(31):51542-51550. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17935. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881666 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of circulating tumour cells-biology and biomarkers.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar;11(3):129-44. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.253. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24445517 Review.
-
Persistent lineage plasticity driving lung cancer development and progression.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70458. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70458. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40847555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating and disseminated tumour cells - mechanisms of immune surveillance and escape.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar;14(3):155-167. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.144. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27644321 Review.
References
-
- Pantel K, Muller V, Auer M, Nusser N, Harbeck N, Braun S. Detection and clinical implications of early systemic tumor cell dissemination in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:6326–6334. - PubMed
-
- Stathopoulou A, Vlachonikolis I, Mavroudis D, Perraki M, Kouroussis C, Apostolaki S, Malamos N, Kakolyris S, Kotsakis A, Xenidis N, Reppa D, Georgoulias V. Molecular detection of cytokeratin-19-positive cells in the peripheral blood of patients with operable breast cancer: evaluation of their prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3404–3412. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.08.135. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xenidis N, Perraki M, Kafousi M, Apostolaki S, Bolonaki I, Stathopoulou A, Kalbakis K, Androulakis N, Kouroussis C, Pallis T, Christophylakis C, Argyraki K, Lianidou ES, Stathopoulos S, Georgoulias V, Mavroudis D. Predictive and prognostic value of peripheral blood cytokeratin-19 mRNA-positive cells detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction in node-negative breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3756–3762. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.5948. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

