BioGPS: an extensible and customizable portal for querying and organizing gene annotation resources
- PMID: 19919682
- PMCID: PMC3091323
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-11-r130
BioGPS: an extensible and customizable portal for querying and organizing gene annotation resources
Abstract
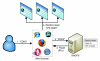
Online gene annotation resources are indispensable for analysis of genomics data. However, the landscape of these online resources is highly fragmented, and scientists often visit dozens of these sites for each gene in a candidate gene list. Here, we introduce BioGPS http://biogps.gnf.org, a centralized gene portal for aggregating distributed gene annotation resources. Moreover, BioGPS embraces the principle of community intelligence, enabling any user to easily and directly contribute to the BioGPS platform.
Figures

References
-
- Flicek P, Aken BL, Beal K, Ballester B, Caccamo M, Chen Y, Clarke L, Coates G, Cunningham F, Cutts T, Down T, Dyer SC, Eyre T, Fitzgerald S, Fernandez-Banet J, Graf S, Haider S, Hammond M, Holland R, Howe KL, Howe K, Johnson N, Jenkinson A, Kahari A, Keefe D, Kokocinski F, Kulesha E, Lawson D, Longden I, Megy K. et al. Ensembl 2008. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D707–714. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

