Systematisation of spatial uncertainties for comparison between a MR and a CT-based radiotherapy workflow for prostate treatments
- PMID: 19919713
- PMCID: PMC2781017
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-54
Systematisation of spatial uncertainties for comparison between a MR and a CT-based radiotherapy workflow for prostate treatments
Abstract
Background: In the present work we compared the spatial uncertainties associated with a MR-based workflow for external radiotherapy of prostate cancer to a standard CT-based workflow. The MR-based workflow relies on target definition and patient positioning based on MR imaging. A solution for patient transport between the MR scanner and the treatment units has been developed. For the CT-based workflow, the target is defined on a MR series but then transferred to a CT study through image registration before treatment planning, and a patient positioning using portal imaging and fiducial markers.
Methods: An "open bore" 1.5T MRI scanner, Siemens Espree, has been installed in the radiotherapy department in near proximity to a treatment unit to enable patient transport between the two installations, and hence use the MRI for patient positioning. The spatial uncertainty caused by the transport was added to the uncertainty originating from the target definition process, estimated through a review of the scientific literature. The uncertainty in the CT-based workflow was estimated through a literature review.
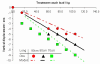
Results: The systematic uncertainties, affecting all treatment fractions, are reduced from 3-4 mm (1Sd) with a CT based workflow to 2-3 mm with a MR based workflow. The main contributing factor to this improvement is the exclusion of registration between MR and CT in the planning phase of the treatment.
Conclusion: Treatment planning directly on MR images reduce the spatial uncertainty for prostate treatments.
Figures

References
-
- Hawighorst H, Debus J, Schreiber W, Knopp MV, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Essig M, Brix G, van Kaick G. Contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer imaging: improvement of brain tumor conspicuity and delineation for radiosurgical target volume definition. Radiother Oncol. 1997;43(3):261–7. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(97)00068-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

