Liver-specific ablation of integrin-linked kinase in mice results in enhanced and prolonged cell proliferation and hepatomegaly after phenobarbital administration
- PMID: 19920070
- PMCID: PMC2807039
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp281
Liver-specific ablation of integrin-linked kinase in mice results in enhanced and prolonged cell proliferation and hepatomegaly after phenobarbital administration
Abstract
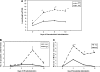
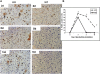
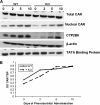
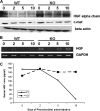
We have recently demonstrated that disruption of extracellular matrix (ECM)/integrin signaling via elimination of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in hepatocytes interferes with signals leading to termination of liver regeneration. This study investigates the role of ILK in liver enlargement induced by phenobarbital (PB). Wild-type (WT) and ILK:liver-/- mice were given PB (0.1% in drinking water) for 10 days. Livers were harvested on 2, 5, and 10 days during PB administration. In the hepatocyte-specific ILK/liver-/- mice, the liver:body weight ratio was more than double as compared to 0 h at day 2 (2.5 times), while at days 5 and 10, it was enlarged three times. In the WT mice, the increase was as expected from previous literature (1.8 times) and seems to have leveled off after day 2. There were slightly increased proliferating cell nuclear antigen-positive cells in the ILK/liver-/- animals at day 2 as compared to WT after PB administration. In the WT animals, the proliferative response had come back to normal by days 5 and 10. Hepatocytes of the ILK/liver-/- mice continued to proliferate up until day 10. ILK/liver-/- mice also showed increased expression of key genes involved in hepatocyte proliferation at different time points during PB administration. In summary, ECM proteins communicate with the signaling machinery of dividing cells via ILK to regulate hepatocyte proliferation and termination of the proliferative response. Lack of ILK in the hepatocytes imparts prolonged proliferative response not only to stimuli related to liver regeneration but also to xenobiotic chemical mitogens, such as PB.
Figures
References
-
- Block GD, Locker J, Bowen WC, Petersen BE, Katyal S, Strom SC, Riley T, Howard TA, Michalopoulos GK. Population expansion, clonal growth, and specific differentiation patterns in primary cultures of hepatocytes induced by HGF/SF, EGF and TGF alpha in a chemically defined (HGM) medium. J. Cell Biol. 1996;132:1133–1149. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carthew P, Edwards RE, Nolan BM. The quantitative distinction of hyperplasia from hypertrophy in hepatomegaly induced in the rat liver by phenobarbital. Toxicol. Sci. 1998;44:46–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

