Antibodies against Manalpha1,2-Manalpha1,2-Man oligosaccharide structures recognize envelope glycoproteins from HIV-1 and SIV strains
- PMID: 19920089
- PMCID: PMC2815653
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwp184
Antibodies against Manalpha1,2-Manalpha1,2-Man oligosaccharide structures recognize envelope glycoproteins from HIV-1 and SIV strains
Abstract
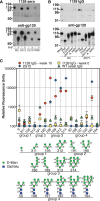
Design of an envelope glycoprotein (Env)-based vaccine against human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) is complicated by the large number of N-linked glycans that coat the protein and serve as a barrier to antibody-mediated neutralization. Compared to normal mammalian glycoproteins, high-mannose-type glycans are disproportionately represented on the gp120 subunit of Env. These N-glycans serve as a target for a number of anti-HIV molecules that bind terminal alpha1,2-linked mannose residues, including lectins and the monoclonal antibody 2G12. We created a Saccharomyces cerevisiae glycosylation mutant, Deltamnn1Deltamnn4, to expose numerous terminal Manalpha1,2-Man residues on endogenous hypermannosylated glycoproteins in the yeast cell wall. Immunization of rabbits with whole cells from this mutant induced antibodies that bound to a broad range of Env proteins, including clade A, B, and C of HIV and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). The gp120 binding activity of these immune sera was due to mannose-specific immunoglobulin, as removal of high-mannose glycans and alpha1,2-linked mannoses from gp120 abrogated serum binding. Glycan array analysis with purified IgG demonstrated binding mainly to glycans with Manalpha1,2-Manalpha1,2-Man trisaccharides. Altogether, these data demonstrate the immunogenicity of exposed polyvalent Manalpha1,2-Manalpha1,2-Man structures on the yeast cell wall mannan and their ability to induce antibodies that bind to the HIV Env protein. The yeast strain and sera from this study will be useful tools for determining the type of mannose-specific response that is needed to develop neutralizing antibodies to the glycan shield of HIV.
Figures



References
-
- Astronomo RD, Lee HK, Scanlan CN, Pantophlet R, Huang CY, Wilson IA, Blixt O, Dwek RA, Wong CH, Burton DR. A glycoconjugate antigen based on the recognition motif of a broadly neutralizing human immunodeficiency virus antibody, 2G12, is immunogenic but elicits antibodies unable to bind to the self glycans of gp120. J Virol. 2008;82:6359–6368. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballou CE. Isolation, characterization, and properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mnn mutants with nonconditional protein glycosylation defects. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:440–470. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini J. Targeting the glycans of gp120: A novel approach aimed at the Achilles heel of HIV. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:726–731. - PubMed
-
- Burton DR, Desrosiers RC, Doms RW, Koff WC, Kwong PD, Moore JP, Nabel GJ, Sodroski J, Wilson IA, Wyatt RT. HIV vaccine design and the neutralizing antibody problem. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:233–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

