Randomized trial and pharmacokinetic study of pegfilgrastim versus filgrastim after dose-intensive chemotherapy in young adults and children with sarcomas
- PMID: 19920107
- PMCID: PMC2787766
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0761
Randomized trial and pharmacokinetic study of pegfilgrastim versus filgrastim after dose-intensive chemotherapy in young adults and children with sarcomas
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the effectiveness, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics of a single dose of pegfilgrastim to daily filgrastim in children and young adults with sarcomas treated with dose-intensive combination chemotherapy.
Experimental design: Patients were randomized to receive a single dose of 100 mcg/kg of pegfilgrastim s.c. or 5 mcg/kg/day of filgrastim s.c., daily until neutrophil recovery after two treatment cycles with vincristine, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (VDC) and two cycles of etoposide and ifosfamide (IE). The duration of severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count, < or =500/mcL) during cycles 1 to 4 and cycle duration for all cycles were compared. Pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim and filgrastim and CD34+ stem cell mobilization were studied on cycle 1. Growth factor-related toxicity, transfusions, and episodes of fever and neutropenia and infections were collected for cycles 1 to 4.
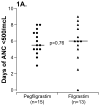
Results: Thirty-four patients (median age, 20 years; range 3.8-25.8) were enrolled, and 32 completed cycles 1 to 4. The median (range) duration of absolute neutrophil count of <500/mcL was 5.5 (3-8) days for pegfilgrastim and 6 (0-9) days for filgrastim (P = 0.76) after VDC, and 1.5 (0-4) days for pegfilgrastim and 3.75 (0-6.5) days for filgrastim (P = 0.11) after IE. More episodes of febrile neutropenia and documented infections occurred on the filgrastim arm. Serum pegfilgrastim concentrations were highly variable. Pegfilgrastim apparent clearance (11 mL/h/kg) was similar to that reported in adults.
Conclusion: A single dose per cycle of pegfilgrastim was well tolerated and may be as effective as daily filgrastim based on the duration of severe neutropenia and number of episodes of febrile neutropenia and documented infections after dose-intensive treatment with VDC and IE.
Figures





References
-
- Johnston E, Crawford J, Blackwell S, et al. Randomized, dose-escalation study of SD/01 compared with daily filgrastim in patients receiving chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(13):2522–8. - PubMed
-
- Zamboni WC. Pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim. Pharmacotherapy. 2003;23(8 Pt 2):9S–14S. - PubMed
-
- Molineux G. The design and development of pegfilgrastim (PEG-rmetHuG-CSF, Neulasta) Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(11):1235–44. - PubMed
-
- Green MD, Koelbl H, Baselga J, et al. A randomized double-blind multicenter phase III study of fixed-dose single-administration pegfilgrastim versus daily filgrastim in patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2003;14(1):29–35. - PubMed
-
- Holmes FA, O’Shaughnessy JA, Vukelja S, et al. Blinded, randomized, multicenter study to evaluate single administration pegfilgrastim once per cycle versus daily filgrastim as an adjunct to chemotherapy in patients with high-risk stage II or stage III/IV breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(3):727–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

