ELM: the status of the 2010 eukaryotic linear motif resource
- PMID: 19920119
- PMCID: PMC2808914
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1016
ELM: the status of the 2010 eukaryotic linear motif resource
Abstract
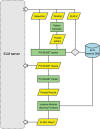
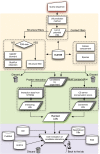
Linear motifs are short segments of multidomain proteins that provide regulatory functions independently of protein tertiary structure. Much of intracellular signalling passes through protein modifications at linear motifs. Many thousands of linear motif instances, most notably phosphorylation sites, have now been reported. Although clearly very abundant, linear motifs are difficult to predict de novo in protein sequences due to the difficulty of obtaining robust statistical assessments. The ELM resource at http://elm.eu.org/ provides an expanding knowledge base, currently covering 146 known motifs, with annotation that includes >1300 experimentally reported instances. ELM is also an exploratory tool for suggesting new candidates of known linear motifs in proteins of interest. Information about protein domains, protein structure and native disorder, cellular and taxonomic contexts is used to reduce or deprecate false positive matches. Results are graphically displayed in a 'Bar Code' format, which also displays known instances from homologous proteins through a novel 'Instance Mapper' protocol based on PHI-BLAST. ELM server output provides links to the ELM annotation as well as to a number of remote resources. Using the links, researchers can explore the motifs, proteins, complex structures and associated literature to evaluate whether candidate motifs might be worth experimental investigation.
Figures

References
-
- Diella F, Haslam N, Chica C, Budd A, Michael S, Brown NP, Trave G, Gibson TJ. Understanding eukaryotic linear motifs and their role in cell signaling and regulation. Front. Biosci. 2008;13:6580–6603. - PubMed
-
- Neduva V, Russell RB. Peptides mediating interaction networks: new leads at last. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006;17:465–471. - PubMed
-
- Petsalaki E, Russell RB. Peptide-mediated interactions in biological systems: new discoveries and applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008;19:344–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

