Characterization of the mycobacterial AdnAB DNA motor provides insights into the evolution of bacterial motor-nuclease machines
- PMID: 19920138
- PMCID: PMC2807320
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076133
Characterization of the mycobacterial AdnAB DNA motor provides insights into the evolution of bacterial motor-nuclease machines
Abstract
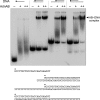
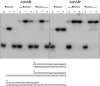
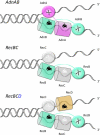
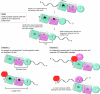
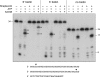
Mycobacterial AdnAB exemplifies a family of heterodimeric motor-nucleases involved in processing DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). The AdnA and AdnB subunits are each composed of an N-terminal UvrD-like motor domain and a C-terminal RecB-like nuclease module. Here we conducted a biochemical characterization of the AdnAB motor, using a nuclease-inactivated heterodimer. AdnAB is a vigorous single strand DNA (ssDNA)-dependent ATPase (k(cat) 415 s(-1)), and the affinity of the motor for the ssDNA cofactor increases 140-fold as DNA length is extended from 12 to 44 nucleotides. Using a streptavidin displacement assay, we demonstrate that AdnAB is a 3' --> 5' translocase on ssDNA. AdnAB binds stably to DSB ends. In the presence of ATP, the motor unwinds the DNA duplex without requiring an ssDNA loading strand. We integrate these findings into a model of DSB unwinding in which the "leading" AdnB and "lagging" AdnA motor domains track in tandem, 3' to 5', along the same DNA single strand. This contrasts with RecBCD, in which the RecB and RecD motors track in parallel along the two separated DNA single strands. The effects of 5' and 3' terminal obstacles on ssDNA cleavage by wild-type AdnAB suggest that the AdnA nuclease receives and processes the displaced 5' strand, while the AdnB nuclease cleaves the displaced 3' strand. We present evidence that the distinctive "molecular ruler" function of the ATP-dependent single strand DNase, whereby AdnAB measures the distance from the 5'-end to the sites of incision, reflects directional pumping of the ssDNA through the AdnAB motor into the AdnB nuclease. These and other findings suggest a scenario for the descent of the RecBCD- and AddAB-type DSB-processing machines from an ancestral AdnAB-like enzyme.
Figures
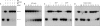
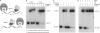

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

