Differential regulation of kainate receptor trafficking by phosphorylation of distinct sites on GluR6
- PMID: 19920140
- PMCID: PMC2807338
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.081141
Differential regulation of kainate receptor trafficking by phosphorylation of distinct sites on GluR6
Abstract
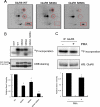
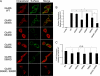
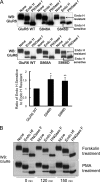
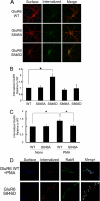
Kainate receptors are widely expressed in the brain, and are present at pre- and postsynaptic sites where they play a prominent role in synaptic plasticity and the regulation of network activity. Within individual neurons, kainate receptors of different subunit compositions are targeted to various locations where they serve distinct functional roles. Despite this complex targeting, relatively little is known about the molecular mechanisms regulating kainate receptor subunit trafficking. Here we investigate the role of phosphorylation in the trafficking of the GluR6 kainate receptor subunit. We identify two specific residues on the GluR6 C terminus, Ser(846) and Ser(868), which are phosphorylated by protein kinase C (PKC) and dramatically regulate GluR6 surface expression. By using GluR6 containing phosphomimetic and nonphosphorylatable mutations for these sites expressed in heterologous cells or in neurons lacking endogenous GluR6, we show that phosphorylation of Ser(846) or Ser(868) regulates receptor trafficking through the biosynthetic pathway. Additionally, Ser(846) phosphorylation dynamically regulates endocytosis of GluR6 at the plasma membrane. Our findings thus demonstrate that phosphorylation of PKC sites on GluR6 regulates surface expression of GluR6 at distinct intracellular trafficking pathways, providing potential molecular mechanisms for the PKC-dependent regulation of synaptic kainate receptor function observed during various forms of synaptic plasticity.
Figures



References
-
- Lerma J., Paternain A. V., Rodríguez-Moreno A., López-García J. C. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 971–998 - PubMed
-
- Vignes M., Collingridge G. L. (1997) Nature 388, 179–182 - PubMed
-
- Castillo P. E., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. (1997) Nature 388, 182–186 - PubMed
-
- Chittajallu R., Vignes M., Dev K. K., Barnes J. M., Collingridge G. L., Henley J. M. (1996) Nature 379, 78–81 - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Moreno A., Herreras O., Lerma J. (1997) Neuron 19, 893–901 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

