The anti-apoptotic protein HAX-1 is a regulator of cardiac function
- PMID: 19920172
- PMCID: PMC2791603
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0906998106
The anti-apoptotic protein HAX-1 is a regulator of cardiac function
Abstract
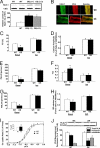
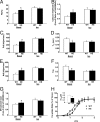
The HS-1 associated protein X-1 (HAX-1) is a ubiquitously expressed protein that protects cardiomyocytes from programmed cell death. Here we identify HAX-1 as a regulator of contractility and calcium cycling in the heart. HAX-1 overexpression reduced sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase (SERCA2) pump activity in isolated cardiomyocytes and in vivo, leading to depressed myocyte calcium kinetics and mechanics. Conversely, downregulation of HAX-1 enhanced calcium cycling and contractility. The inhibitory effects of HAX-1 were abolished upon phosphorylation of phospholamban, which plays a fundamental role in controlling basal contractility and constitutes a key downstream effector of the beta-adrenergic signaling cascade. Mechanistically, HAX-1 promoted formation of phospholamban monomers, the active/inhibitory units of the calcium pump. Indeed, ablation of PLN rescued HAX-1 inhibition of contractility in vivo. Thus, HAX-1 represents a regulatory mechanism in cardiac calcium cycling and its responses to sympathetic stimulation, implicating its importance in calcium homeostasis and cell survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dash R, et al. Interactions between phospholamban and beta-adrenergic drive may lead to cardiomyopathy and early mortality. Circulation. 2001;103:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Haghighi K, et al. Superinhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum function by phospholamban induces cardiac contractile failure. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:24145–24152. - PubMed
-
- Zhai J, et al. Cardiac-specific overexpression of a superinhibitory pentameric phospholamban mutant enhances inhibition of cardiac function in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10538–10544. - PubMed
-
- MacLennan DH, Kranias EG. Phospholamban: A crucial regulator of cardiac contractility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:566–577. - PubMed
-
- Vafiadaki E, et al. Phospholamban interacts with HAX-1, a mitochondrial protein with anti-apoptotic function. J Mol Biol. 2007;367:65–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

