Definition of early transcriptional circuitry involved in light-induced reversal of PIF-imposed repression of photomorphogenesis in young Arabidopsis seedlings
- PMID: 19920208
- PMCID: PMC2798328
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.070672
Definition of early transcriptional circuitry involved in light-induced reversal of PIF-imposed repression of photomorphogenesis in young Arabidopsis seedlings
Abstract
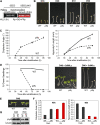
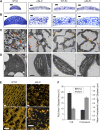
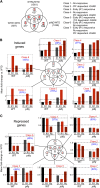
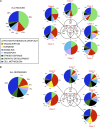
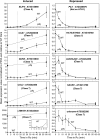
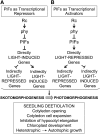
Light signals perceived by the phytochromes induce the transition from skotomorphogenic to photomorphogenic development (deetiolation) in dark-germinated seedlings. Evidence that a quadruple mutant (pifq) lacking four phytochrome-interacting bHLH transcription factors (PIF1, 3, 4, and 5) is constitutively photomorphogenic in darkness establishes that these factors sustain the skotomorphogenic state. Moreover, photoactivated phytochromes bind to and induce rapid degradation of the PIFs, indicating that the photoreceptor reverses their constitutive activity upon light exposure, initiating photomorphogenesis. Here, to define the modes of transcriptional regulation and cellular development imposed by the PIFs, we performed expression profile and cytological analyses of pifq mutant and wild-type seedlings. Dark-grown mutant seedlings display cellular development that extensively phenocopies wild-type seedlings grown in light. Similarly, 80% of the gene expression changes elicited by the absence of the PIFs in dark-grown pifq seedlings are normally induced by prolonged light in wild-type seedlings. By comparing rapidly light-responsive genes in wild-type seedlings with those responding in darkness in the pifq mutant, we identified a subset, enriched in transcription factor-encoding genes, that are potential primary targets of PIF transcriptional regulation. Collectively, these data suggest that the transcriptional response elicited by light-induced PIF proteolysis is a major component of the mechanism by which the phytochromes pleiotropically regulate deetiolation and that at least some of the rapidly light-responsive genes may comprise a transcriptional network directly regulated by the PIF proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Sady, B., Ni, W., Kircher, S., Schafer, E., and Quail, P.H. (2006). Photoactivated phytochrome induces rapid PIF3 phosphorylation prior to proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol. Cell 23 439–446. - PubMed
-
- Bae, G., and Choi, G. (2008). Decoding of light signals by plant phytochromes and their interacting proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59 281–311. - PubMed
-
- Bajracharya, D., and Schopfer, P. (1979). Effect of light on the development of glyoxysomal functions in the cotyledons of mustard (Sinapis alba L.) seedlings. Planta 145 181–186. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, D., Viczian, A., Kircher, S., Nobis, T., Nitschke, R., Kunkel, T., Panigrahi, K.C., Adam, E., Fejes, E., Schafer, E., and Nagy, F. (2004). Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16 1433–1445. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

