The Arabidopsis B-box zinc finger family
- PMID: 19920209
- PMCID: PMC2798317
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.069088
The Arabidopsis B-box zinc finger family
Figures
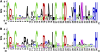
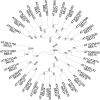
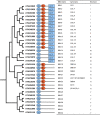
Similar articles
-
The GATA family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice.Plant Physiol. 2004 Apr;134(4):1718-32. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037788. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15084732 Free PMC article.
-
The snail superfamily of zinc-finger transcription factors.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;3(3):155-66. doi: 10.1038/nrm757. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11994736 Review.
-
The Dof domain, a zinc finger DNA-binding domain conserved only in higher plants, truly functions as a Cys2/Cys2 Zn finger domain.Plant J. 2004 Mar;37(5):741-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2003.01997.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 14871313
-
Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome.BMC Genomics. 2004 Jul 5;5(1):39. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-39. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15236668 Free PMC article.
-
The tify family previously known as ZIM.Trends Plant Sci. 2007 Jun;12(6):239-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.04.004. Epub 2007 May 10. Trends Plant Sci. 2007. PMID: 17499004 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of B-box zinc finger (BBX) gene family in Medicago sativa and their roles in abiotic stress responses.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jan 24;25(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10036-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38267840 Free PMC article.
-
The BBX gene CmBBX22 negatively regulates drought stress tolerance in chrysanthemum.Hortic Res. 2022 Aug 25;9:uhac181. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac181. eCollection 2022. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 36338842 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of B-Box Gene Family and Candidate Light-Related Member Analysis of Tung Tree (Vernicia fordii).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1977. doi: 10.3390/ijms25041977. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396654 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of B-box proteins and VvBBX44 involved in light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape (Vitis vinifera L.).Planta. 2021 May 1;253(5):114. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03618-z. Planta. 2021. PMID: 33934247
-
The sweet potato B-box transcription factor gene IbBBX28 negatively regulates drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 29;13:1077958. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1077958. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36523761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang, C.S., Li, Y.H., Chen, L.-T., Chen, W.-C., Hsieh, W.-P., Shin, J., Jane, W.-N., Chou, S.-J., Choi, G., Hu, J.-M., Somerville, S., and Wu, S.-H. (2008). LZF1, a HY5-regulated transcriptional factor, functions in Arabidopsis de-etiolation. Plant J. 54 205–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

