A novel microRNA targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans
- PMID: 19920351
- PMCID: PMC2786801
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI39832
A novel microRNA targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2010 Jan;120(1):395. Liao, Er-Yuan [removed]
Abstract
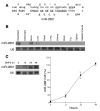
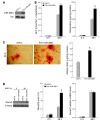
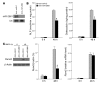
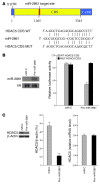
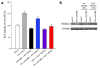
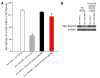
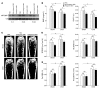
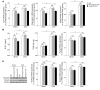
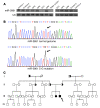
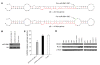
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) interfere with translation of specific target mRNAs and are thought to thereby regulate many cellular processes. Recent studies have suggested that miRNAs might play a role in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Here, we identify a new miRNA (miR-2861) in primary mouse osteoblasts that promotes osteoblast differentiation by repressing histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) expression at the post-transcriptional level. miR-2861 was found to be transcribed in ST2 stromal cells during bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced (BMP2-induced) osteogenesis, and overexpression of miR-2861 enhanced BMP2-induced osteoblastogenesis, whereas inhibition of miR-2861 expression attenuated it. HDAC5, an enhancer of runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) degradation, was confirmed to be a target of miR-2861. In vivo silencing of miR-2861 in mice reduced Runx2 protein expression, inhibited bone formation, and decreased bone mass. Importantly, miR-2861 was found to be conserved in humans, and a homozygous mutation in pre-miR-2861 that blocked expression of miR-2861 was shown to cause primary osteoporosis in 2 related adolescents. Consistent with the mouse data, HDAC5 levels were increased and Runx2 levels decreased in bone samples from the 2 affected individuals. Thus, our studies show that miR-2861 plays an important physiological role in osteoblast differentiation and contributes to osteoporosis via its effect on osteoblasts.
Figures
Comment in
-
Bone: novel microRNA expressed in osteoblasts promotes bone formation.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Feb;6(2):64. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.268. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20976863 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A Runx2/miR-3960/miR-2861 regulatory feedback loop during mouse osteoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 8;286(14):12328-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.176099. Epub 2011 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21324897 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-103a functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit bone formation through targeting Runx2.J Bone Miner Res. 2015 Feb;30(2):330-45. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2352. J Bone Miner Res. 2015. PMID: 25195535
-
Circulating miR-374b-5p negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation in the progression of osteoporosis via targeting Wnt3 AND Runx2.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Mar-Apr;34(2):345-355. doi: 10.23812/19-507-A-9. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 32548991
-
MicroRNA functions in osteogenesis and dysfunctions in osteoporosis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013 Jun;11(2):72-82. doi: 10.1007/s11914-013-0143-6. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013. PMID: 23605904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in bone development.Bone. 2021 Feb;143:115760. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115760. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Bone. 2021. PMID: 33220505 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Bone Biology and Osteoporosis: Can They Drive Therapeutic Choices?Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 12;17(8):1329. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081329. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27529237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-30 family members negatively regulate osteoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7503-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.292722. Epub 2012 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22253433 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-22 promotes osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by repressing HDAC6 protein expression.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Sep 1;21(13):2531-40. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0014. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22375943 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs as Developmental Regulators.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jul 1;7(7):a008144. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008144. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26134312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood levels of microRNAs associated with ischemic heart disease differ between Austrians and Japanese: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 12;10(1):13628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69332-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32788621 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

