Glycogen synthase kinase-3: a new therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 19920820
- PMCID: PMC2795437
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605437
Glycogen synthase kinase-3: a new therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is highly resistant to chemotherapy because of a high apoptotic threshold. Recent evidences suggest that GSK-3beta positively regulates human pancreatic cancer and leukaemia cell survival in part through regulation of nuclear factor (NF-kappaB)-mediated expression of anti-apoptotic molecules. Our objectives were to determine the expression pattern of GSK-3beta and to assess the anti-cancer effect of GSK-3beta inhibition in RCC.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry and nuclear/cytosolic fractionation were performed to determine the expression pattern of GSK-3beta in human RCCs. We used small molecule inhibitor, RNA interference, western blotting, quantitative RT-PCR, BrDU incorporation and MTS assays to study the effect of GSK-3beta inactivation on renal cancer cell proliferation and survival.
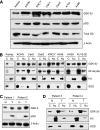
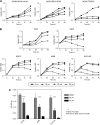
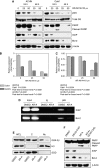
Results: We detected aberrant nuclear accumulation of GSK-3beta in RCC cell lines and in 68 out of 74 (91.89%) human RCCs. We found that pharmacological inhibition of GSK-3 led to a decrease in proliferation and survival of renal cancer cells. We observed that inhibition of GSK-3 results in decreased expression of NF-kappaB target genes Bcl-2 and XIAP and a subsequent increase in renal cancer cell apoptosis. Moreover, we show that GSK-3 inhibitor and Docetaxel synergistically suppress proliferation and survival of renal cancer cells.
Conclusions: Our results show nuclear accumulation of GSK-3beta as a new marker of human RCC, identify that GSK-3 positively regulates RCC cell survival and proliferation and suggest inhibition of GSK-3 as a new promising approach in the treatment of human renal cancer.
Figures



References
-
- An J, Sun Y, Fisher M, Rettig MB (2004) Maximal apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is nuclear factor-kappaB dependent. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 727–736 - PubMed
-
- Beck SDW, Patel MI, Snyder ME, Kattan MW, Motzer RJ, Reuter VE, Russo P (2004) Effect of papillary and chromophobe cell type on disease-free survival after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 11: 71–77 - PubMed
-
- Bhat R, Xue Y, Berg S, Hellberg S, Ormo M, Nilsson Y, Radesater A-C, Jerning E, Markgren P-O, Borgegard T, Nylof M, Gimenez-Cassina A, Hernandez F, Lucas JJ, Diaz-Nido J, Avila J (2003) Structural insights and biological effects of glycogen synthase kinase 3-specific inhibitor AR-A014418. J Biol Chem 278: 45937–45945 - PubMed
-
- Bilim V, Kawasaki T, Katagiri A, Wakatsuki S, Takahashi K, Tomita Y (2000) Altered expression of beta-catenin in renal cell cancer and transitional cell cancer with the absence of beta-catenin gene mutations. Clin Cancer Res 6: 460–466 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

