Submucosal injection solution for gastrointestinal tract endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection
- PMID: 19920900
- PMCID: PMC2761197
- DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s3219
Submucosal injection solution for gastrointestinal tract endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection
Abstract
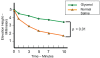
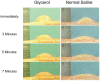
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) have provided new alternatives for minimally invasive treatment of gastrointestinal adenomas and early-stage cancers that involve a minimum risk of lymph-node metastasis. The use of submucosal injections is essential to the success of these endoscopic resection techniques. The "ideal" submucosal injection solution should provide a sufficiently high submucosal fluid cushion for safe and effective EMRs and ESDs while also preserving lesion tissue for accurate histopathological assessment. In the past, normal saline (NS) solution was commonly used for this purpose, but it is difficult to achieve the proper submucosal elevation and maintain the desired height with NS. Therefore, other safe and effective facilitative submucosal injection solutions have been developed that also take into account relevant cost-benefit considerations. This review examines recent advances in the development of effective submucosal injection solutions for use during endoscopic resections.
Keywords: endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR); endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD); gastrointestinal tract; submucosal injection solution.
Figures
References
-
- Burns JW, Colt MJ, Burgees LS, et al. Preclinical evaluation of Seprafilm bioresorbable membrane. Eur J Surg Suppl. 1997;577:40–8. - PubMed
-
- Conio M, Rajan E, Sorbi D, et al. Comparative performance in the porcine esophagus of different solutions used for submucosal injection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:513–16. - PubMed
-
- Feitoza AB, Gostout CJ, Burgart LJ, et al. Hydroxypropyl methyl-cellulose: A better submucosal fluid cushion for endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:41–7. - PubMed
-
- Folwaczny C, Heldwein W, Obermaier G, et al. Influence of prophylactic local administration of epinephrine on bleeding complications after polypectomy. Endoscopy. 1997;29:31–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

