Comparative in vivo bioequivalence and in vitro dissolution of two valproic acid sustained-release formulations
- PMID: 19920901
- PMCID: PMC2761171
- DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s3556
Comparative in vivo bioequivalence and in vitro dissolution of two valproic acid sustained-release formulations
Abstract
Objective: A study was conducted to establish the bioequivalence between different sustained-release formulations of valproic acid (Depakene R and Selenica R), which were developed in Japan.
Materials and methods: The clinical investigation was designed in a randomized, crossover fashion with a single dose given to 12 healthy subjects. The subjects were administered a single 600 mg dose of valproic acid in one of two formulations. Serial venous blood samples were obtained over 72 hours after each administration to measure valproic acid in serum by enzyme immunoassay (EIA). In addition, a dissolution test was performed. Each sample was analyzed by an high-performance liquid chromatography to determine the dissolution rate of valproic acid.
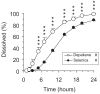
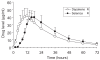
Results: No difference in maximum concentration or area under the curve was found between the two formulations. The time to maximum concentration of the new formation was significantly delayed compared with the conventional formulation (10.8 +/- 1.7 versus 17.6 +/- 1.8 hours, p < 0.001). Apparent clearance or elimination half-life did not differ between the two formulations. An in vitro dissolution study showed that Depakene R was significantly more dissoluble than Selenica R.
Conclusion: Based on the results, the present study demonstrated a significant difference between the two sustained-release formulations in the absorption profile, and also demonstrated that the bioavailability of valproic acid in the two formulations was similar but absorption speed (lag time) was very different.
Keywords: Depakene R; Selenica R; bioequivalence; sustained-release; valproic acid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different serum concentrations of steady-state valproic acid in two sustained-release formulations.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2007 Jun;61(3):308-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2007.01656.x. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17472600
-
Bioequivalence of a new sustained-release formulation of sodium valproate, valproate modified-release granules, compared with existing sustained-release formulations after once- or twice-daily administration.Pharmacotherapy. 2005 Jan;25(1):35-41. doi: 10.1592/phco.25.1.35.55626. Pharmacotherapy. 2005. PMID: 15767218 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative in vivo bioequivalence and in vitro dissolution of two cyclosporin A soft gelatin capsule formulations.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Feb;45(2):126-32. doi: 10.5414/cpp45126. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17323793 Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of the bioequivalence of two formulations of clarithromycin extended-release 500-mg tablets under fasting and fed conditions: a single-dose, randomized, open-label, two-period, two-way crossover study in healthy Jordanian male volunteers.Clin Ther. 2008 Oct;30(10):1831-43. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.10.010. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 19014838 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic properties and bioequivalence of 2 formulations of valsartan 160-mg tablets: A randomized, single-dose, 2-period crossover study in healthy Korean male volunteers.Clin Ther. 2014 Feb 1;36(2):273-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.01.004. Clin Ther. 2014. PMID: 24529292 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bialer M. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of sustained release formulations of antiepileptic drugs. Clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Bowden CL, Singh V. Valproate in bipolar disorder: 2000 onwards. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2005;426:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Buck D, Jacoby A, Baker GA, et al. Factors influencing compliance with antiepileptic drug regimes. Seizure. 1997;6:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Cramer J, Vachon L, Desforges C, et al. Dose frequency and dose interval compliance with multiple antiepileptic medications during a controlled clinical trial. Epilepsia. 1995;36:1111–7. - PubMed
-
- Doughty J, Baker GA, Jacoby A, et al. Compliance and satisfaction with switching from an immediate-release to sustained-release formulation of valproate in people with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2003;4:710–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

